Earth:Tributary
A tributary,[1] or affluent,[2] is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake.[3] A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean.[4] Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainage basin of its surface water and groundwater, leading the water out into an ocean. The Irtysh is a chief tributary of the Ob river and is also the longest tributary river in the world with a length of 4,248 km (2,640 mi). The Madeira River is the largest tributary river by volume in the world with an average discharge of 31,200 m3/s (1.1 million cu ft/s).
A confluence, where two or more bodies of water meet, usually refers to the joining of tributaries.
The opposite to a tributary is a distributary, a river or stream that branches off from and flows away from the main stream.[5] Distributaries are most often found in river deltas.
Terminology
"Right tributary", or "right-bank tributary", and "left tributary", or "left-bank tributary", are terms stating the orientation of the tributary relative to the flow of the main stem river. These terms are defined from the perspective of looking downstream (in the direction the water current of the main stem is going).[6]
An early tributary is a tributary that joins the main stem river closer to the main river's source than its end. Similarly, a "late tributary" joins the main river much further downstream, closer to the main river's end point.
In the U.S., where tributaries sometimes have the same name as the river into which they feed, they are called forks. These are typically designated by compass direction. For example, the American River in California receives flow from its North, Middle, and South forks. The Chicago River's North Branch has the East, West, and Middle Fork; the South Branch has its South Fork, and used to have a West Fork as well (now filled in).
Forks are sometimes designated as right or left. Here, the handedness is from the point of view of an observer facing upstream. For instance, Steer Creek has a left tributary which is called Right Fork Steer Creek.
Ordering and enumeration
Tributaries are sometimes listed starting with those nearest to the source of the river and ending with those nearest to the mouth of the river. The Strahler stream order examines the arrangement of tributaries in a hierarchy of first, second, third and higher orders, with the first-order tributary being typically the least in size. For example, a second-order tributary would be the result of two or more first-order tributaries combining to form the second-order tributary.[6]
Another method is to list tributaries from mouth to source, in the form of a tree structure, stored as a tree data structure.[citation needed]
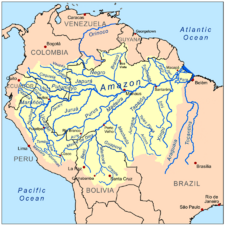
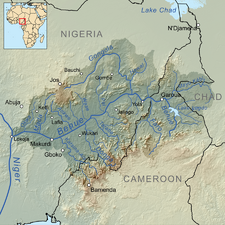
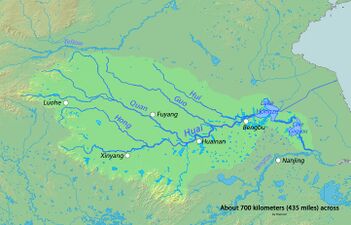
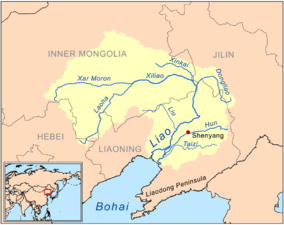
Gallery
- A gallery of major river basins with tributaries
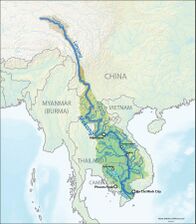
The Mekong is a trans-boundary river, originating in the Tibetan Plateau. Its upper tributary river systems (e.g. ngom chu) are restricted to narrow gorges, but the tributaries that feed its lower reaches (e.g. the Mun River) cover larger areas.
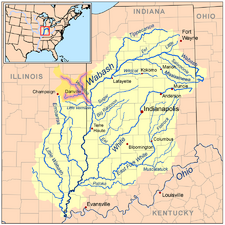
The water basin of the Wabash River; the other rivers (not including the Ohio River) are tributaries of the Wabash River. The Vermillion River (and its forks) is a highlighted example of a tributary of the Wabash River. The Wabash River is also a tributary of the Ohio River, which in turn is a tributary of the Mississippi River.
See also
References
- ↑ "tributary". PhysicalGeography.net, Michael Pidwirny & Scott Jones, 2009. Viewed 17 September 2012.
- ↑ "affluent". The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company, 2004. Viewed 30 September 2008.
- ↑ "Definition of TRIBUTARY". Definition of TRIBUTARY. https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/tributary.
- ↑ Krebs, Robert E. (2003). The Basics of Earth Science. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-313-31930-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=-4ndyH7u6T0C&pg=PA179.
- ↑ "opposite to a tributary". PhysicalGeography.net, Michael Pidwirny & Scott Jones, 2009. Viewed 17 September 2012.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Bisson, Peter and Wondzell, Steven. "Olympic Experimental State Forest Synthesis of Riparian Research and Monitoring", United States Forest Service, p. 15 (1 December 2009).
 |