Chemistry:Sulfur tetrafluoride
| |||
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sulfur(IV) fluoride
| |||
| Other names
Sulfur tetrafluoride
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2418 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| SF4 | |||
| Molar mass | 108.07 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | colorless gas | ||
| Density | 1.95 g/cm3, −78 °C | ||
| Melting point | −121.0 °C | ||
| Boiling point | −38 °C | ||
| reacts | |||
| Vapor pressure | 10.5 atm (22 °C)[1] | ||
| Structure | |||
| Seesaw (C2v) | |||
| 0.632 D[2] | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | highly toxic corrosive | ||
| Safety data sheet | ICSC 1456 | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
none[1] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
C 0.1 ppm (0.4 mg/m3)[1] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D.[1] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions
|
Sulfur dichloride Disulfur dibromide Sulfur trifluoride | ||
Other cations
|
Oxygen difluoride Selenium tetrafluoride Tellurium tetrafluoride | ||
Related sulfur fluorides
|
Disulfur difluoride Sulfur difluoride Disulfur decafluoride Sulfur hexafluoride | ||
Related compounds
|
Thionyl fluoride | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Sulfur tetrafluoride is the chemical compound with the formula SF4. It is a colorless corrosive gas that releases dangerous HF upon exposure to water or moisture. Despite these unwelcome characteristics, this compound is a useful reagent for the preparation of organofluorine compounds,[3] some of which are important in the pharmaceutical and specialty chemical industries.
Structure
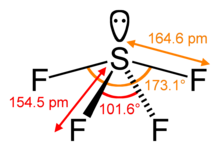
Sulfur in SF4 is in the formal +4 oxidation state. Of sulfur's total of six valence electrons, two form a lone pair. The structure of SF4 can therefore be anticipated using the principles of VSEPR theory: it is a see-saw shape, with S at the center. One of the three equatorial positions is occupied by a nonbonding lone pair of electrons. Consequently, the molecule has two distinct types of F ligands, two axial and two equatorial. The relevant bond distances are S–Fax = 164.3 pm and S–Feq = 154.2 pm. It is typical for the axial ligands in hypervalent molecules to be bonded less strongly. In contrast to SF4, the related molecule SF6 has sulfur in the 6+ state, no valence electrons remain nonbonding on sulfur, hence the molecule adopts a highly symmetrical octahedral structure. Further contrasting with SF4, SF6 is extraordinarily inert chemically.
The 19F NMR spectrum of SF4 reveals only one signal, which indicates that the axial and equatorial F atom positions rapidly interconvert via pseudorotation.[4]
Synthesis and manufacture
At the laboratory scale, fluorination of elemental sulfur with cobaltic fluoride suffices:[5]
- S + 4CoF3 → SF4 + 4CoF2
For larger-scale syntheses, SF4 is produced by the reaction of SCl2 and NaF in acetonitrile:[6]
- 3 SCl2 + 4 NaF → SF4 + S2Cl2 + 4 NaCl
At higher temperatures (e.g. 225–450 °C), the solvent is superfluous. Moreover, sulfur dichloride may be replaced by elemental sulfur (S) and chlorine (Cl2).[7][8]
A low-temperature (e.g. 20–86 °C) alternative to the chlorinative process above uses liquid bromine (Br2) as oxidant and solvent:[9]
- S(s) + 2 Br2(l; excess) + 4KF(s) → SF4↑ + 4 KBr(brom)
Use of SF4 for the synthesis of fluorocarbons
In organic synthesis, SF4 is used to convert COH and C=O groups into CF and CF2 groups, respectively.[10] Certain alcohols readily give the corresponding fluorocarbon. Ketones and aldehydes give geminal difluorides. The presence of protons alpha to the carbonyl leads to side reactions and diminished (30–40%) yield. Also diols can give cyclic sulfite esters, (RO)2SO. Carboxylic acids convert to trifluoromethyl derivatives. For example, treatment of heptanoic acid with SF4 at 100–130 °C produces 1,1,1-trifluoroheptane. Hexafluoro-2-butyne can be similarly produced from acetylenedicarboxylic acid. The coproducts from these fluorinations, including unreacted SF4 together with SOF2 and SO2, are toxic but can be neutralized by their treatment with aqueous KOH.
The use of SF4 is being superseded in recent years by the more conveniently handled diethylaminosulfur trifluoride, Et2NSF3, "DAST", where Et = CH3CH2.[11] This reagent is prepared from SF4:[12]
- SF4 + Me3SiNEt2 → Et2NSF3 + Me3SiF
Other reactions
Sulfur chloride pentafluoride (SF5Cl), a useful source of the SF5 group, is prepared from SF4.[13]
Hydrolysis of SF4 gives sulfur dioxide:[14]
- SF4 + 2 H2O → SO2 + 4 HF
This reaction proceeds via the intermediacy of thionyl fluoride, which usually does not interfere with the use of SF4 as a reagent.[6]
Toxicity
SF4 reacts inside the lungs with moisture, generating sulfur dioxide and hydrogen fluoride:[15]
- SF4 + 2 H2O → SO2 + 4 HF
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0580". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0580.html.
- ↑ Tolles, W. M.; W. M. Gwinn, W. D. (1962). "Structure and Dipole Moment for SF4". J. Chem. Phys. 36 (5): 1119–1121. doi:10.1063/1.1732702. Bibcode: 1962JChPh..36.1119T.
- ↑ Wang, C.-L. J. (2004). Paquette, L.. ed. Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. New York: J. Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/047084289X. ISBN 9780471936237.
- ↑ Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. (2001). Inorganic Chemistry. San Diego: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ↑ Kwasnik, W. (1963). "Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry". in Brauer, Georg. Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 1 (2nd ed.). NY, NY: Academic Press. https://archive.org/details/Handbook_of_Preparative_Inorganic_Chemistry_1_2_Brauer/page/n191/.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Fawcett, F. S.; Tullock, C. W. (1963). Sulfur (IV) Fluoride: (Sulfur Tetrafluoride). Inorganic Syntheses. 7. pp. 119–124. doi:10.1002/9780470132388.ch33.
- ↑ Tullock, C. W.; Fawcett, F. S.; Smith, W. C.; Coffman, D. D. (1960). "The Chemistry of Sulfur Tetrafluoride. I. The Synthesis of Sulfur Tetrafluoride". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 82 (3): 539–542. doi:10.1021/ja01488a011.
- ↑ Tullock, C.W., "Synthesis of Sulfur Tetrafluoride", US patent 2992073, issued 1961
- ↑ Winter, R.W.; Cook P.W. (2010). "A simplified and efficient bromine-facilitated SF4-preparation method". J. Fluorine Chem. 131: 780-783. doi:10.1016/j.jfluchem.2010.03.016
- ↑ Hasek, W. R.. "1,1,1-Trifluoroheptane". Organic Syntheses. http://www.orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=cv5p1082.; Collective Volume, 5, pp. 1082
- ↑ Fauq, A. H. (2004). Paquette, L.. ed. Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. New York: J. Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/047084289X. ISBN 9780471936237..
- ↑ W. J. Middleton; E. M. Bingham. "Diethylaminosulfur Trifluoride". Organic Syntheses. http://www.orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=cv6p0440.; Collective Volume, 6, pp. 440
- ↑ Nyman, F.; Roberts, H. L.; Seaton, T. (1966). "Sulfur Chloride Pentafluoride". Inorganic Syntheses. Inorganic Syntheses. 8. McGraw-Hill. p. 160. doi:10.1002/9780470132395.ch42. ISBN 9780470132395.
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ↑ Johnston, H. (2003). A Bridge not Attacked: Chemical Warfare Civilian Research During World War II. World Scientific. pp. 33–36. ISBN 981-238-153-8.
ja:フッ化硫黄#四フッ化硫黄
 |