Biology:Nandidae
| Asian leaffish | |
|---|---|
| |
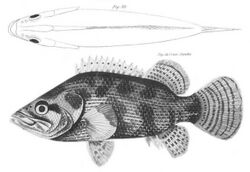
| Gangetic leaffish Nandus nandus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Clade: | Percomorpha |
| Family: | Nandidae Bleeker, 1852 |
| Genera[1] | |
|
see text | |
Nandidae, the leaffish, are a family of small freshwater fishes which some authorities classify in the order Anabantiformes, but which the 5th edition of Fishes of the World classifies the family and the related Badidae and Pristolepididae outside that order as "sister-taxa". Fishes of the World classified these families and the Anabantiformes alongside Synbranchiformes, Carangiformes, Istiophoriformes and Pleuronectiformes in a monophyletic clade which is a sister taxon to the Ovalentaria but to which the authors do not assign a rank or a name.[2] According to FishBase, the family includes three genera: Nandus of South and Southeast Asia with several species, and the monotypic Afronandus and Polycentropsis of tropical West and Middle Africa.[1] Most recent authorities place the two African genera in the South American leaffish family, Polycentridae, which is only distantly related to Nandus (the "true" Nandidae).[3] Another Asian family, Pristolepididae, share the common name leaffish and appear to be more closely related.[4]
These fish usually have a coloration that appears to have evolved to resemble dead leaves, and very large protractile mouths. Those features, along with their peculiar movements (seemingly intended to resemble a leaf innocently moving through the water) help them to catch fairly large prey compared to their body size, including small fish, aquatic insects, and other invertebrates. They tend to stay in one place and wait for prey; they are "lie-in-wait" predators.
Their odd, leaf-like appearance and unusual behavior make them interesting to aquarium hobbyists.
Genera
There are three genera in the family:[1][5]
- Afronandus Meinken, 1955
- Nandus Valenciennes, 1831
- Polycentropsis Boulenger, 1901
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Froese, Rainer, and Daniel Pauly, eds. (2014). "Nandidae" in FishBase. February 2014 version.
- ↑ J. S. Nelson; T. C. Grande; M. V. H. Wilson (2016). Fishes of the World (5th ed.). Wiley. pp. 394. ISBN 978-1-118-34233-6. https://sites.google.com/site/fotw5th/.
- ↑ Collins, R.A., R. Britz, and L. Ruber (2015). Phylogenetic systematics of leaffishes (Teleostei: Polycentridae, Nandidae). J Zoolog Syst Evol Res 53(4). doi:10.1111/jzs.12103
- ↑ Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2019). Species of Pristolepis in FishBase. February 2019 version.
- ↑ Eschmeyer, William N.; Fricke, Ron; van der Laan, Richard, eds. "Genera in the family Nandidae". California Academy of Sciences. http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/fishcatget.asp?tbl=genus&family=Nandidae.
Wikidata ☰ Q426300 entry
 |

