Chemistry:Allysine
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
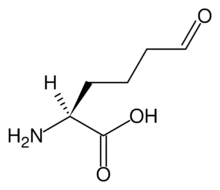
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2S)-2-Amino-6-oxohexanoic acid | |
| Other names
2-aminoadipate semialdehyde, 2-amino-5-formylvaleric acid, norvaline, 6-oxo-DL-norleucine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | allysine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H11NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 145.158 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | unstable |
| Density | 1.74g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 295.2 °C (563.4 °F; 568.3 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 132.3 °C (270.1 °F; 405.4 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Allysine is a derivative of lysine that features a formyl group in place of the terminal amine. The free amino acid does not exist, but the allysine residue does. It is produced by aerobic oxidation of lysine residues by the enzyme lysyl oxidase. The transformation is an example of a post-translational modification. The semialdehyde form exists in equilibrium with a cyclic derivative.[1]
Allysine is involved in the production of elastin and collagen.[2] Increased allysine concentration in tissues has been correlated to the presence of fibrosis.[3]
Allysine residues react with sodium 2-naphthol-6-sulfonate to produce a fluorescent bis-naphtol-allysine product.[4] In another assay, allysine-containing proteins are reduced with sodium borohydride to give a peptide containing the 6-hydroxynorleucine (6-hydroxy-2-aminocaproic acid) residue, which (unlike allysine) is stable to proteolysis.[1]
Further reading
- "Formation of allysine in β-lactoglobulin and myofibrillar proteins by glyoxal and methylglyoxal: Impact on water-holding capacity and in vitro digestibility". Food Chemistry 271: 87–93. January 2019. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.07.167. PMID 30236745.
- "Allysine and α-Aminoadipic Acid as Markers of the Glyco-Oxidative Damage to Human Serum Albumin under Pathological Glucose Concentrations". Antioxidants 10 (3): 474. March 2021. doi:10.3390/antiox10030474. PMID 33802856.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Requena, J. R.; Levine, R. L.; Stadtman, E. R. (2003). "Recent Advances in the Analysis of Oxidized Proteins". Amino Acids 25 (3–4): 221–226. doi:10.1007/s00726-003-0012-1. PMID 14661085.
- ↑ Eyre, David R.; Paz, Mercedes A.; Gallop, Paul M. (1984). "Cross-Linking in Collagen and Elastin". Annual Review of Biochemistry 53: 717–748. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003441. PMID 6148038.
- ↑ "68Ga-NODAGA-Indole: An Allysine-Reactive Positron Emission Tomography Probe for Molecular Imaging of Pulmonary Fibrogenesis". Journal of the American Chemical Society 141 (14): 5593–5596. April 2019. doi:10.1021/jacs.8b12342. PMID 30908032.
- ↑ "High sensitivity HPLC method for determination of the allysine concentration in tissue by use of a naphthol derivative". Journal of Chromatography. B, Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences 1064: 7–13. October 2017. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.08.032. PMID 28886479.
 |


