Chemistry:Rhodium acetylacetonate
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(E)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one;rhodium
| |
| Other names
Rhodium(III) acetylacetonate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H21O6Rh | |
| Molar mass | 400.232 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | orange solid |
| Melting point | 260 °C (500 °F; 533 K) (decomposes) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H312, H315, H319, H332, H335, H361 | |
| P201, P202, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P281, P301+312, P302+352, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P308+313, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P363, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
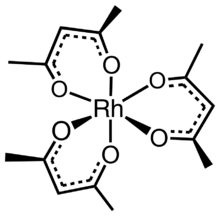
Rhodium acetylacetonate is the coordination complex with the formula Rh(C
5H
7O
2)
3, which is sometimes known as Rh(acac)3. The molecule has D3-symmetry. It is a yellow-orange solid that is soluble in organic solvents.
It is prepared from RhCl3(H2O)3 and acetylacetone.[1] The complex has been resolved into individual enantiomers by separation of its adduct with dibenzoyltartaric acid.[2]
Related compounds
- Dicarbonyl(acetylacetonato)rhodium(I), Rh(C
5H
7O
2)(CO)
2 - Iridium acetylacetonate, Ir(C
5H
7O
2)
3
References
- ↑ James E. Collins, Michael P. Castellani, Arnold L. Rheingold, Edward J. Miller, William E. Geiger, Anne L. Rieger, Philip H. Rieger "Synthesis, Characterization, and Molecular Structure of Bis(tetraphenylcyclopentdienyl)rhodium(II)" Organometallics 1995, pp 1232–1238. doi:10.1021/om00003a025
- ↑ Drake, A. F.; Gould, J. M.; Mason, S. F.; Rosini, C.; Woodley, F. J. (1983). "The optical resolution of tris(pentane-2,4-dionato)metal(III) complexes". Polyhedron 2 (6): 537–538. doi:10.1016/S0277-5387(00)87108-9.
 |

