Biology:Afraflacilla
Afraflacilla is a genus of the spider family Salticidae (jumping spiders).[1][2][3] Most species are distributed in Eastern to Northern Africa (including the Middle East) and Australia, with two species (A. epiblemoides and A. tarajalis) found in Europe.
Spiders in this genus can produce sounds by rubbing a part of its leg against the head, using specialized structures, a process called stridulation. Some African species, both adults and juveniles, use their stridulatory organs for social communal behaviour.[4]
Afraflacilla in Australia
Afraflacilla species in Australia include A. grayorum, A. gunbar, A. huntorum, A. milledgei, A. stridulator, A. vestjensi and A. yeni. In Australia they occupy tree trunks in deserts, savanna woodland and in open sclerophyll forests from south west Western Australia to Cape York Queensland, mostly in warmer regions. There are many undescribed Australian species. Afraflacilla grayorum Grays' stridulating jumping spider, found in northern Australian deserts, was named in honour of Michael and Greta Gray.[5]
Description

Afraflacilla are small to medium-sized spiders, ranging in body length from 3 to 6 mm.[4]
The cephalothorax is rectangular with curved sides when viewed from above and low to very low from the side. A curved row of 12 or more stridulatory tubercles extends from below the anterior lateral eye to below the posterior lateral eye. These spiny tubercles correspond with opposing structures on the femur of the first leg.[4]
Afraflacilla species have tubercles and bristles (on the sides of the carapace near the eyes and on their legs) which they rub together to make sounds used in courtship and possibly defence. The line of small tubercles (sharp knobs) under the eyes on the side of the carapace are usually visible to the naked eye.[6] The tubercles on the femur are rubbed against those on the side of the head to produce sound. Chelicerae are rather long, vertical, with two marginal teeth.[4]
The abdomen is elliptical to elongate-ovate, somewhat squared-off at the front.[4]
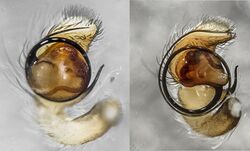
The first pair of legs is much larger than the others, sometimes huge and stout in comparison, sometimes very hairy and sometimes with a very large spur underneath the enlarged tibia.[4]
The male palpal organ of many Australian Afraflacilla species has a large, circling embolus (inseminating sclerite) and retro-lateral tibial apophysis (side spike). Some undescribed Australian Afraflacilla species have greatly enlarged segments of the first pair of legs, and sometimes massive spurs coming from underneath the tibia and metatarsus (third and second last leg segments). Enlarged leg-one segments are also a feature of Pseudicius, a genus widespread outside Australia.[5]
Taxonomy
This genus was for a time included in the genus Pseudicius, and the boundaries between both genera are disputed. In 2016 Jerzy Prószyński erected the genus Psenuc for some borderline species.[1][7] The name Afraflacilla is combined from Africa, where most earlier described species were found, and Flacilla Simon, 1901, an obsolete salticid genus now called Flacillula Strand, 1932. This genus name is in turn derived from Aelia Flaccilla, wife of Roman Emperor Theodosius I. Afraflacilla, Pseudicius, Festucula and Marchena are close relatives and form a monophyletic group.
Species
-
male A. altera
-
female A. bipunctata
-
female A. braunsi
-
female A. elegans
As of October 2025[update], this genus includes 51 species:[1]
- Afraflacilla adavathurensis Sampathkumar & Caleb, 2023 – India
- Afraflacilla albopunctata Wesołowska & Russell-Smith, 2022 – Guinea, Ivory Coast
- Afraflacilla altera (Wesołowska, 2000) – Botswana, Zimbabwe, South Africa
- Afraflacilla antineae (Denis, 1954) – Algeria
- Afraflacilla arabica Wesołowska & van Harten, 1994 – Egypt, Yemen, Iran, Afghanistan
- Afraflacilla asorotica (Simon, 1890) – Libya, Israel, Saudi Arabia, Yemen
- Afraflacilla ballarini Cao & Li, 2016 – China
- Afraflacilla bamakoi Berland & Millot, 1941 – Mali (type species)
- Afraflacilla banni Prajapati, Tatu & Kamboj, 2021 – India
- Afraflacilla berlandi Denis, 1955 – Libya
- Afraflacilla bipunctata (G. W. Peckham & E. G. Peckham, 1903) – South Africa
- Afraflacilla braunsi (G. W. Peckham & E. G. Peckham, 1903) – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen, United Arab Emirates, Turkmenistan
- Afraflacilla datuntata (Logunov & Zamanpoore, 2005) – Afghanistan
- Afraflacilla elegans (Wesołowska & Cumming, 2008) – Zimbabwe, South Africa
- Afraflacilla epiblemoides (Chyzer, 1891) – Central, Eastern Europe, Turkey, Armenia
- Afraflacilla eximia (Wesołowska & Russell-Smith, 2000) – Tanzania
- Afraflacilla fayda (Wesołowska & van Harten, 2010) – United Arab Emirates
- Afraflacilla flavipes (Caporiacco, 1935) – Turkmenistan, Pakistan
- Afraflacilla goaensis Gawas & Tripathi, 2024 – India
- Afraflacilla grayorum Żabka, 1993 – Australia (Western Australia, Queensland)
- Afraflacilla gunbar Żabka & Gray, 2002 – Australia (New South Wales)
- Afraflacilla histrionica (Simon, 1902) – South Africa
- Afraflacilla huntorum Żabka, 1993 – Australia (Western Australia, Victoria)
- Afraflacilla imitator (Wesołowska & Haddad, 2013) – South Africa
- Afraflacilla javanica (Prószyński & Deeleman-Reinhold, 2012) – Indonesia (Java)
- Afraflacilla karinae (Haddad & Wesołowska, 2011) – South Africa
- Afraflacilla kerala Babu, Tripathi & Caleb, 2023 – India
- Afraflacilla kraussi (Marples, 1964) – Marshall Islands, Cook Islands, Samoa
- Afraflacilla kurichiadensis Sudhin, Nafin & Sudhikumar, 2022 – India
- Afraflacilla matabelensis (Wesołowska, 2011) – Namibia, Zimbabwe, South Africa
- Afraflacilla miajlarensis Tripathi, Jangid, Prajapati & Siliwal, 2022 – India
- Afraflacilla mikhailovi (Prószyński, 2000) – Israel
- Afraflacilla mushrif (Wesołowska & van Harten, 2010) – United Arab Emirates
- Afraflacilla philippinensis (Prószyński, 1992) – Philippines
- Afraflacilla refulgens (Wesołowska & Cumming, 2008) – Zimbabwe
- Afraflacilla reiskindi (Prószyński, 1992) – Borneo
- Afraflacilla risbeci Berland & Millot, 1941 – Senegal, Guinea
- Afraflacilla roberti (Wesołowska, 2011) – Kenya
- Afraflacilla scenica Denis, 1955 – Niger
- Afraflacilla sengwaensis (Wesołowska & Cumming, 2011) – Zimbabwe
- Afraflacilla similis Berland & Millot, 1941 – Senegal
- Afraflacilla spiniger (O. Pickard-Cambridge, 1872) – Egypt to South Sudan
- Afraflacilla stridulator Żabka, 1993 – Australia (Western Australia)
- Afraflacilla tamaricis (Simon, 1885) – North Africa, Israel, Saudi Arabia, Yemen
- Afraflacilla tarajalis Miñano & Tamajón, 2017 – Spain, Portugal, Morocco, Greece (Crete)
- Afraflacilla venustula (Wesołowska & Haddad, 2009) – Mozambique, South Africa
- Afraflacilla vespae Wawer & Wesołowska, 2025 – Ghana
- Afraflacilla vestjensi Żabka, 1993 – Australia (Northern Territory)
- Afraflacilla wadis (Prószyński, 1989) – Saudi Arabia, Israel, Yemen
- Afraflacilla yeni Żabka, 1993 – Australia (Victoria)
- Afraflacilla zuluensis (Haddad & Wesołowska, 2013) – South Africa
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Gen. Afraflacilla Berland & Millot, 1941". World Spider Catalog. doi:10.24436/2. https://wsc.nmbe.ch/genus/2477. Retrieved 2025-10-07.
- ↑ Żabka, Marek (1993). "Salticidae (Arachnida: Araneae) of the Oriental, Australian and Pacific Regions. IX.* Genera Afrajlacilla Berland & Millot 1941 and Evarcha Simon 1902". Invertebrate Taxonomy 7 (2): 279–295. doi:10.1071/it9930279.
- ↑ Żabka, Marek (2002). "Salticidae (Arachnida: Araneae) from Oriental, Australian and Pacific regions, XVI. New species of Grayenulla and Afraflacilla.". Records of the Australian Museum 54 (3): 269–274. doi:10.3853/j.0067-1975.54.2002.1366.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 Dippenaar-Schoeman, A.S.; Van der Walt, V.; Haddad, C.R.; Foord, S.H.; Lotz, L.N. (2025). The Salticidae of South Africa. Part 1 (A-Den). Version 1. South African National Survey of Arachnida Photo Identification Guide. p. 7. doi:10.5281/zenodo.15222559.
 This article incorporates text available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "ARACHNE.ORG.AU". http://www.arachne.org.au/01_cms/advanced_search.asp?varKeyword=afraflacilla&action=search&imageField.x=0&imageField.y=0.
- ↑ Whyte, Robert (2017). A Field Guide to Spiders of Australia CSIRO. Australia: CSIRO Publishing. ISBN 9780643107076.
- ↑ Prószyński, Jerzy (2016). "Delimitation and description of 19 new genera, a subgenus and a species of Salticidae (Araneae) of the world.". Ecologica Montenegrina 7: 4–32. doi:10.37828/em.2016.7.1.
Wikidata ☰ Q117705 entry
 |




