Biology:Glehnia
| Glehnia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Apiales |
| Family: | Apiaceae |
| Subfamily: | Apioideae |
| Tribe: | Selineae |
| Genus: | Glehnia F.Schmidt |
| Species: | G. littoralis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Glehnia littoralis F. Schmidt ex Miq.
| |
Glehnia is a genus of plants in the carrot family, Apiaceae. It is monotypic, being represented by the single species, Glehnia littoralis,[1] commonly known as beach silvertop and American silvertop. The genus was named after Russian botanist Peter von Glehn.[2]
Description
It is a long-taprooted plant forming a basal patch of leaves, with each leaf made up of several rounded, lobular segments. It reaches a maximum height exceeding .5 metres (1 1⁄2 feet), with the North American subspecies only reported to reach 6.5 centimetres (2 1⁄2 inches).[3] The plant's erect stem is topped with an umbel of carrotlike white flowers.
Chemistry
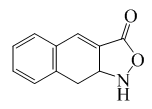
The plant contains naphthisoxazole A.[4]
Taxonomy
Two subspecies exist, one in Asia and one in North America; the latter is named leiocarpa.[3]
Distribution and habitat
It is native to eastern Asia, particularly eastern China, Japan, and far-eastern Russia, and western North America from Alaska to northern California . It can be found on sandy beaches and dunes.[3]
Uses
The plant is perhaps best known as a Chinese herbal remedy for cough.[5]
References
- ↑ Wu Zhengyi (1983). "On the significance of Pacific intercontinental discontinuity". Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden 70 (4): 577–590. doi:10.2307/2398977. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/part/31100.
- ↑ "White Flowers". Netarts Bay Today http://netartsbaytoday.org. http://netartsbaytoday.org/html/white_flowers.html.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Spellenberg, Richard (2001). National Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Wildflowers: Western Region (rev ed.). Knopf. pp. 340. ISBN 978-0-375-40233-3. https://archive.org/details/nationalaudubons00spel/page/340/.
- ↑ Li G.Q. (2008). "A new isoxazol from Glehnia littoralis". Fitoterapia 79 (3): 238–239. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2008.01.002. PMID 18325682.
- ↑ Tang, Weici and Eisenbrand, Gerhard Handbook of Chinese Medicinal Plants : Chemistry, Pharmacology, Toxicology, pub. Wiley-VCH 2011 ISBN:978-3-527-32226-8 Vol.1 pps. 599-600 Glehnia littoralis.
External links
- {{citation
| mode = cs1 | title = Glehnia | work = Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN) | url = | publisher = [[Organization:Agricultural Research ServAgricultural Research Service (ARS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) | access-date = }}
Wikidata ☰ Q2576002 entry
 |