Biology:Cupressus macnabiana
| Cupressus macnabiana | |
|---|---|

| |
| Cupressus macnabiana foliage | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Gymnospermae |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Cupressales |
| Family: | Cupressaceae |
| Genus: | Cupressus |
| Species: | C. macnabiana
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cupressus macnabiana A.Murray bis
| |
| |
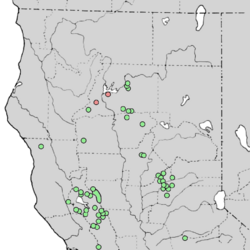
| Natural range | |
| |
| (Red circles indicate extinct populations.) | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
Cupressus macnabiana (MacNab cypress or Shasta cypress) is a species of cypress in western North America.[3]
Distribution
Cupressus macnabiana is endemic to northern California . Cupressus macnabiana is one of the most widely distributed of all the native California cypresses, found growing in chaparral, oak woodlands, and coniferous woodlands habitats along the inner northern California Coast Ranges and the foothills of the northern Sierra Nevada. MacNab cypress is often associated with ultramafic soils.[4]
Description
Cupressus macnabiana is an evergreen shrub or small tree, 3–12 metres (9.8–39.4 ft) (rarely to 17 metres (56 ft)) tall, with a spreading crown that is often broader than it is tall. The foliage is produced in dense, short flat sprays (unlike most other California cypresses, which do not have flattened sprays), bright glaucous gray-green, with a strong spicy-resinous scent. The leaves are scale-like, 1–2 mm long with an acute apex, and a conspicuous white resin gland on the center of the leaf. Young seedlings produce needle-like leaves up to 10 mm (0.4 inches) long in their first year.[5]
The seed cones are oblong-ovoid to cuboid, 15–25 mm long and 13–20 mm broad, with six (rarely four or eight) scales, each scale bearing a prominent umbo; they are strongly serotinous, not opening to release the seeds until the parent tree is killed by wildfire. This enables heavy seed release to colonize the bare, fire-cleared ground. The pollen cones are 3–4 mm long, and release their pollen in the fall.[5]
See also
- California interior chaparral and woodlands- (subecoregion)
- Fire ecology
References
- ↑ Farjon, A. (2013). "Cupressus macnabiana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2013: e.T42222A2962703. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2013-1.RLTS.T42222A2962703.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/42222/2962703. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ The Plant List, Cupressus macnabiana A.Murray bis
- ↑ A. Farjon. 2005. A Monograph of Cupressaceae and Sciadopityaceae. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. ISBN:1-84246-068-4.
- ↑ C. Michael Hogan. 2010. Leather Oak, Quercus durata. Encyclopedia of Earth. National Council for Science and Environment. Washington DC
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Flora of North America: Cupressus macnabiana
- Farjon, A. (2013). "Cupressus macnabiana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2013: e.T42222A2962703. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2013-1.RLTS.T42222A2962703.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/42222/2962703. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- Stuart, J. D.; J. O. Sawyer (2001). Trees and Shrubs of California. University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-22110-9.
- Wolf, C. B. & Wagener, W. E. (1948). The New World cypresses. El Aliso 1: 195-205.
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q1144379 entry
 |



