Milü
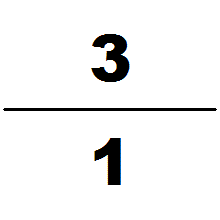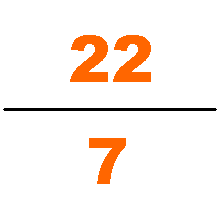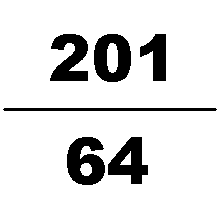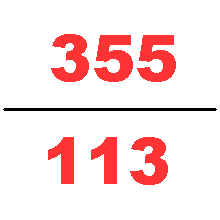
| Milü |
|---|
Milü (Chinese: 密率; pinyin: mìlǜ; "close ratio"), also known as Zulü (Zu's ratio), is the name given to an approximation to π (pi) found by Chinese mathematician and astronomer Zu Chongzhi in the 5th century. Using Liu Hui's algorithm (which is based on the areas of regular polygons approximating a circle), Zu famously computed π to be between 3.1415926 and 3.1415927[lower-alpha 1] and gave two rational approximations of π, 22/7 and 355/113, naming them respectively Yuelü (Chinese: 约率; pinyin: yuēlǜ; "approximate ratio") and Milü.[1]
355/113 is the best rational approximation of π with a denominator of four digits or fewer, being accurate to six decimal places. It is within 0.000009% of the value of π, or in terms of common fractions overestimates π by less than 1/3748629. The next rational number (ordered by size of denominator) that is a better rational approximation of π is 52163/16604, though it is still only correct to six decimal places. To be accurate to seven decimal places, one needs to go as far as 86953/27678. For eight, 102928/32763 is needed.[2]
The accuracy of Milü to the true value of π can be explained using the continued fraction expansion of π, the first few terms of which are [3; 7, 15, 1, 292, 1, 1, ...]. A property of continued fractions is that truncating the expansion of a given number at any point will give the "best rational approximation" to the number. To obtain Milü, truncate the continued fraction expansion of π immediately before the term 292; that is, π is approximated by the finite continued fraction [3; 7, 15, 1], which is equivalent to Milü. Since 292 is an unusually large term in a continued fraction expansion (corresponding to the next truncation introducing only a very small term, 1/292, to the overall fraction), this convergent will be especially close to the true value of π:[3]
An easy mnemonic helps memorize this useful fraction by writing down each of the first three odd numbers twice: 1 1 3 3 5 5, then dividing the decimal number represented by the last 3 digits by the decimal number given by the first three digits. Alternatively, 1/π ≈ 113⁄355.
Zu's contemporary calendarist and mathematician He Chengtian invented a fraction interpolation method called "harmonization of the divisor of the day" (Chinese: :zh:调日法; pinyin: diaorifa) to increase the accuracy of approximations of π by iteratively adding the numerators and denominators of fractions. Zu Chongzhi's approximation π ≈ 355/113 can be obtained with He Chengtian's method.[1]
See also
- Continued fraction expansion of π and its convergents
- Approximations of π
- Pi Approximation Day
Notes
- ↑ Specifically, Zu found that if the diameter of a circle has a length of , then the length of the circle's circumference falls within the range . It is not known what method Zu used to calculate this result.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Martzloff, Jean-Claude (2006). A History of Chinese Mathematics. Springer. p. 281. ISBN 9783540337829. https://archive.org/details/historychinesema00mart_058.
- ↑ "Fractional Approximations of Pi". http://qin.laya.com/tech_projects_approxpi.html.
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W.. "Pi Continued Fraction" (in en). http://mathworld.wolfram.com/PiContinuedFraction.html.
External links
 |
