| Display title | Inverse Gaussian distribution |
| Default sort key | Inverse Gaussian Distribution |
| Page length (in bytes) | 26,640 |
| Namespace ID | 0 |
| Page ID | 182803 |
| Page content language | en - English |
| Page content model | wikitext |
| Indexing by robots | Allowed |
| Number of redirects to this page | 0 |
| Counted as a content page | Yes |
| Page image | 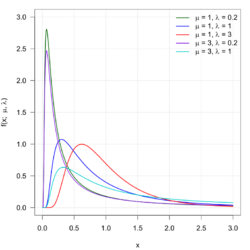 |
| HandWiki item ID | None |
| Edit | Allow all users (infinite) |
| Move | Allow all users (infinite) |
| Page creator | imported>Corlink |
| Date of page creation | 16:53, 8 February 2024 |
| Latest editor | imported>Corlink |
| Date of latest edit | 16:53, 8 February 2024 |
| Total number of edits | 1 |
| Recent number of edits (within past 90 days) | 0 |
| Recent number of distinct authors | 0 |
Description | Content |
Article description: (description)
This attribute controls the content of the description and og:description elements. | In probability theory, the inverse Gaussian distribution (also known as the Wald distribution) is a two-parameter family of continuous probability distributions with support on (0,∞).
Its probability density function is given by
$ f(x;\mu ,\lambda )={\sqrt {\frac {\lambda }{2\pi x^{3}}}}\exp {\biggl... |

