| Display title | Physics:Boudouard reaction |
| Default sort key | Boudouard reaction |
| Page length (in bytes) | 9,146 |
| Namespace ID | 3020 |
| Namespace | Physics |
| Page ID | 669022 |
| Page content language | en - English |
| Page content model | wikitext |
| Indexing by robots | Allowed |
| Number of redirects to this page | 0 |
| Counted as a content page | Yes |
| Page image | 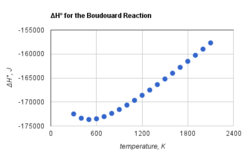 |
| HandWiki item ID | None |
| Edit | Allow all users (infinite) |
| Move | Allow all users (infinite) |
| Page creator | imported>John Stpola |
| Date of page creation | 17:11, 13 July 2022 |
| Latest editor | imported>John Stpola |
| Date of latest edit | 17:11, 13 July 2022 |
| Total number of edits | 1 |
| Recent number of edits (within past 90 days) | 0 |
| Recent number of distinct authors | 0 |
Description | Content |
Article description: (description)
This attribute controls the content of the description and og:description elements. | The Boudouard reaction, named after Octave Leopold Boudouard, is the redox reaction of a chemical equilibrium mixture of carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide at a given temperature. It is the disproportionation of carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide and graphite or its reverse:
2CO ⇌ CO2 + C
The Boudouard... |
