Place:Katima Mulilo: Difference between revisions
(change) |
John Stpola (talk | contribs) (url) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Town in Namibia}} | |||
{{Infobox settlement | {{Infobox settlement | ||
<!--See the Table at Infobox settlement for all fields and descriptions of usage--> | <!--See the Table at Infobox settlement for all fields and descriptions of usage--> | ||
<!-- Basic info ----------------> | <!-- Basic info ---------------->| name = Katima Mulilo | ||
|name | | other_name = | ||
|other_name | | native_name = <!-- for cities whose native name is not in English --> | ||
|native_name | | nickname = Ngweze | ||
|nickname | | settlement_type = Town | ||
|settlement_type | | motto = Luyeme Hamoho (Together we stand) | ||
|motto | <!-- images and maps ----------->| image_skyline = Katima Mulilo Bridge.jpg | ||
<!-- images and maps -----------> | | imagesize = | ||
|image_skyline | | image_caption = Zambezi River | ||
|imagesize | | image_flag = | ||
|image_caption | | flag_size = | ||
|image_flag | | image_seal = | ||
|flag_size | | seal_size = | ||
|image_seal | | image_shield = | ||
|seal_size | | shield_size = | ||
|image_shield | | image_blank_emblem = | ||
|shield_size | | blank_emblem_type = | ||
|image_blank_emblem | | blank_emblem_size = | ||
|blank_emblem_type | | image_map = SchuckmannsburgMap.png | ||
|blank_emblem_size | | mapsize = 300px | ||
|image_map | | map_caption = Katima Mulilo and Luhonono | ||
|mapsize | | pushpin_map = Namibia <!-- the name of a location map as per http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Location_map --> | ||
|map_caption | | pushpin_label_position = bottom | ||
|pushpin_map | | pushpin_mapsize = 300 | ||
|pushpin_label_position = bottom | | pushpin_map_caption = Location in Namibia | ||
|pushpin_mapsize | <!-- Location ------------------>| subdivision_type = Country | ||
|pushpin_map_caption | | subdivision_name = {{flag|Namibia}} | ||
<!-- Location ------------------> | | subdivision_type1 = Region | ||
|subdivision_type | | subdivision_name1 = Zambezi Region | ||
|subdivision_name | | subdivision_type2 = Constituency | ||
|subdivision_type1 | | subdivision_name2 = Katima Mulilo Urban | ||
|subdivision_name1 | | subdivision_type3 = | ||
|subdivision_type2 | | subdivision_name3 = <!-- Politics -----------------> | ||
|subdivision_name2 | | government_footnotes = | ||
|subdivision_type3 | | government_type = Town Council | ||
|subdivision_name3 | | leader_title = Mayor | ||
<!-- Politics -----------------> | | leader_name = John Ntemwa | ||
|government_footnotes | | leader_title1 = <!-- for places with, say, both a mayor and a city manager --> | ||
|government_type | | leader_name1 = | ||
|leader_title | | established_title = Founded | ||
|leader_name | | established_date = 1935 | ||
|leader_title1 | <!-- Area --------------------->| area_magnitude = | ||
|leader_name1 | | unit_pref = Metric | ||
|established_title | | area_footnotes = | ||
|established_date | | area_total_km2 = 44.9 | ||
<!-- Area ---------------------> | | area_land_km2 = 44.9 | ||
|area_magnitude | | area_water_km2 = 0 | ||
|unit_pref | | area_total_sq_mi = <!-- Population -----------------------> | ||
|area_footnotes | | population_as_of = 2023 | ||
|area_total_km2 | | population_footnotes = <ref name=nsa>{{cite web | title=Table 4.2.2 Urban population by Census years (2001 and 2011) | url=http://cms.my.na/assets/documents/p19dmn58guram30ttun89rdrp1.pdf | work=Namibia 2011 – Population and Housing Census Main Report | publisher=Namibia Statistics Agency | access-date=24 August 2016 | page=39}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://nsa.nsa.org.na/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Preliminary-Report-doc-fn.pdf|title=2023 Population & Housing Census Preliminary Report|website=Statistics Namibia|df=dmy|access-date=16 March 2024|archive-date=24 March 2024|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240324152514/https://nsa.nsa.org.na/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Preliminary-Report-doc-fn.pdf|url-status=dead}}</ref> | ||
|area_land_km2 | | population_note = | ||
|area_water_km2 | | population_total = 46,401 | ||
|area_total_sq_mi | | population_density_km2 = 1,033 | ||
<!-- Population -----------------------> | | population_density_sq_mi = | ||
|population_as_of | | population_metro = | ||
|population_footnotes | | population_density_metro_km2 = | ||
|population_note | | population_density_metro_sq_mi = | ||
|population_total | | population_urban = | ||
|population_density_km2 | | population_density_urban_km2 = | ||
|population_density_sq_mi | | population_density_urban_sq_mi = | ||
|population_metro | | population_blank1_title = Ethnicities | ||
|population_density_metro_km2 | | population_blank1 = | ||
|population_density_metro_sq_mi = | | population_density_blank1_km2 = | ||
|population_urban | | population_density_blank1_sq_mi = <!-- General information ---------------> | ||
|population_density_urban_km2 | | timezone = [[Central Africa Time|CAT]] | ||
|population_density_urban_sq_mi = | | utc_offset = +2 | ||
|population_blank1_title | | timezone_DST = | ||
|population_blank1 | | utc_offset_DST = | ||
|population_density_blank1_km2 = | | coordinates = {{coord|17|30|14|S|24|16|30|E|region:NA|display=inline,title}} | ||
|population_density_blank1_sq_mi = | | elevation_footnotes = <!--for references: use tags--> | ||
<!-- General information ---------------> | | elevation_m = 950 | ||
|timezone | | elevation_ft = <!-- Area/postal codes & others --------> | ||
|utc_offset | | postal_code_type = Postal code | ||
|timezone_DST | | postal_code = 20002 | ||
|utc_offset_DST | | area_code = 066 | ||
|coordinates | | blank_name = [[Earth:Köppen climate classification|Climate]] | ||
|elevation_footnotes | | blank_info = [[Earth:Semi-arid climate#Hot semi-arid climates|BSh]] | ||
|elevation_m | | blank1_name = | ||
|elevation_ft | | blank1_info = | ||
<!-- Area/postal codes & others --------> | | website = {{URL|https://kmtc.org.na/}} | ||
|postal_code_type | | footnotes = | ||
|postal_code | |||
|area_code | |||
|blank_name | |||
|blank_info | |||
|blank1_name | |||
|blank1_info | |||
|website | |||
|footnotes | |||
}} | }} | ||
'''Katima Mulilo''' or simply '''Katima''' is the capital of the Zambezi Region in Namibia. It had | '''Katima Mulilo''' or simply '''Katima''' is the capital of the Zambezi Region in Namibia. It had 46,401 inhabitants in 2023,<ref>{{Cite web |title=Namibia: Regions, Towns, Villages & Settlements - Population Statistics, Maps, Charts, Weather and Web Information |url=https://www.citypopulation.de/en/namibia/cities/ |access-date=2024-03-16 |website=www.citypopulation.de}}</ref><ref name=business>{{cite news | ||
|title=Businesses mushroom | |title=Businesses mushroom | ||
|last=Inambao | |last=Inambao | ||
| Line 101: | Line 94: | ||
|publisher=The Cardboard Box | |publisher=The Cardboard Box | ||
|url=http://www.namibian.org/travel/namibia/katima_mulilo.html | |url=http://www.namibian.org/travel/namibia/katima_mulilo.html | ||
|access-date=24 December 2010}}</ref> The town receives | |access-date=24 December 2010 | ||
|archive-date=31 October 2019 | |||
|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191031221641/http://www.namibian.org/travel/namibia/katima_mulilo.html | |||
|url-status=dead | |||
}}</ref> The town receives annual average rainfall of {{convert|654|mm}}.<ref name="Nam2011">{{cite news | |||
|url=http://www.namibian.com.na/news/full-story/archive/2011/may/article/rainy-season-was-one-for-the-record-books/ | |url=http://www.namibian.com.na/news/full-story/archive/2011/may/article/rainy-season-was-one-for-the-record-books/ | ||
|title=Rainy season was one for the record books | |title=Rainy season was one for the record books | ||
| Line 116: | Line 113: | ||
==Economy and infrastructure== | ==Economy and infrastructure== | ||
Established and run as a garrison for a long time, Katima Mulilo still shows signs of its military past | Established and run as a garrison for a long time, Katima Mulilo still shows signs of its military past. In the city centre was the South African Defence Force military base and almost every house had a bomb shelter. The town benefited from the military presence in terms of infrastructure and employment, and there are still a number of military bases surrounding the town.<ref name=SADF>{{cite news | ||
|title=Katima owes its growth to SADF | |title=Katima owes its growth to SADF | ||
|last=Inambao | |last=Inambao | ||
| Line 161: | Line 158: | ||
===Transport=== | ===Transport=== | ||
[[File:Caprivi Highway near Katima aerial.jpg|thumb|left|150px|Crossing the Trans–Caprivi Highway near Katima's Mpacha Airport.]] | [[File:Caprivi Highway near Katima aerial.jpg|thumb|left|150px|Crossing the [[Trans–Caprivi Highway]] near Katima's Mpacha Airport.]] | ||
Katima Mulilo is the terminal town of the Trans–Caprivi Highway, and the highway together with its extension to Zambia is called the Trans-Caprivi Corridor. The Trans–Caprivi Highway was opened in 1999, and the bridge to Sesheke, and with it the entire Trans-Caprivi Corridor, in 2004.<ref>{{cite web | Katima Mulilo is the terminal town of the Trans–Caprivi Highway, and the highway together with its extension to Zambia is called the Trans-Caprivi Corridor. The Trans–Caprivi Highway was opened in 1999, and the bridge to Sesheke, and with it the entire Trans-Caprivi Corridor, in 2004.<ref>{{cite web | ||
|title=Trans–Caprivi Corridor | |title=Trans–Caprivi Corridor | ||
| Line 181: | Line 178: | ||
|publisher=Namibia 1on1 | |publisher=Namibia 1on1 | ||
|url=http://www.namibia-1on1.com/katima-mulilo.html | |url=http://www.namibia-1on1.com/katima-mulilo.html | ||
|access-date=24 December 2010}}</ref> From early days (and before the advent of fire-lighting matches), there was river transport by barge (propelled by paddlers) along the | |access-date=24 December 2010}}</ref> From early days (and before the advent of fire-lighting matches), there was river transport by barge (propelled by paddlers) along the Zambezi from [[Place:Livingstone, Zambia|Livingstone]] to Sesheke,<ref>{{Cite web|title=Betty Clay {{!}} 1936 - 1939 Newly-wed|url=http://www.spanglefish.com/BettyClay/index.asp?pageid=638516|access-date=2021-08-25|website=www.spanglefish.com}}</ref> onwards past the Ngonye Falls at Sioma, where an attempt was made in about 1905 to bypass the Falls with a canal.<ref>{{Cite book | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KWh2S2d68XoC&pg=PA52 |title = An African Trading Empire: The Story of Susman Brothers & Wulfsohn, 1901–2005|isbn = 9781850438533|last1 = MacMillan|first1 = Hugh|last2 = Hugh|first2 = Macmillan|date = 27 May 2005| publisher=Bloomsbury Academic }}</ref> Barges were unloaded and dragged by oxen round the Falls. The route continued to [[Place:Mongu|Mongu]], the administrative capital of [[Place:Barotseland|Barotseland]], and northwards to the settlement of Balovale (now Zambezi) in the North West of Zambia, at {{coords|-13.551|23.115|display=inline}}. When the barge reached Katima Mulilo, the fire was extinguished (but embers kept), and the barge was unloaded and then dragged empty up the rapids, and re-loaded before continuing the journey – but not before the fire was re-lit.{{cn|date=August 2022}} | ||
On 28 January 1935, the administrative centre of the Caprivi Strip was moved from Schuckmannsburg to Katima Mulilo. This date is assumed as the foundation date of Katima Mulilo. The regional office, the only brick-and-mortar building at Katima Mulilo at a time when the area consisted exclusively of pristine forests, was built under a giant [[Biology:Adansonia|Baobab]] situated near today's SWAPO Party regional offices. In present times the tree is known as the ''Toilet Tree'' because of a rest room carved into it.<ref name=history>{{cite news | On 28 January 1935, the administrative centre of the Caprivi Strip was moved from Schuckmannsburg to Katima Mulilo. This date is assumed as the foundation date of Katima Mulilo. The regional office, the only brick-and-mortar building at Katima Mulilo at a time when the area consisted exclusively of pristine forests, was built under a giant [[Biology:Adansonia|Baobab]] situated near today's SWAPO Party regional offices. In present times the tree is known as the ''Toilet Tree'' because of a rest room carved into it.<ref name=history>{{cite news | ||
| Line 190: | Line 187: | ||
|date=December 2010}}</ref> | |date=December 2010}}</ref> | ||
Katima Mulilo was very sparsely populated at that time. It had a [[Religion:Missionary|missionary]] school run by the [[Religion:Seventh-day Adventist Church|Seventh-day Adventists]], and the small settlements were connected only by sleigh tracks. Without any roads nor other infrastructure it was difficult to administer the Caprivi Strip from here. The | Katima Mulilo was very sparsely populated at that time. It had a [[Religion:Missionary|missionary]] school run by the [[Religion:Seventh-day Adventist Church|Seventh-day Adventists]], and the small settlements were connected only by sleigh tracks. Without any roads nor other infrastructure it was difficult to administer the Caprivi Strip from here. The South African administration therefore decided to shift the regional office again, this time to [[Place:Pretoria|Pretoria]], in 1939. Given its proximity to important transport routes, particularly the railway bridge at Victoria Falls, the location of Katima Mulilo became strategically important in the Second World War which broke out soon afterwards. All military supplies, people, and goods had to be flown in. The town's first car arrived in 1940 and belonged to the air strip operator.<ref name=history/> | ||
In 1940, William "Bill" Finaughty established the first shop in the Caprivi Strip in Katima Mulilo; the settlement that surrounded the shop was subsequently named after him. In the 1950s transport on the Zambezi River was established and allowed connection to the train service at [[Place:Livingstone, Zambia|Livingstone]]. The M'pacha Airfield, today Katima Mulilo Airport, was constructed in 1965 at a cost of 65 million [[Finance:South African rand|Rand]], an astronomical amount at that time when 2 Rand roughly equalled 1 [[Finance:Pound sterling|Pound sterling]]. A police station was erected in 1961.<ref name=growth>{{cite news | In 1940, William "Bill" Finaughty established the first shop in the Caprivi Strip in Katima Mulilo; the settlement that surrounded the shop was subsequently named after him. In the 1950s transport on the Zambezi River was established and allowed connection to the train service at [[Place:Livingstone, Zambia|Livingstone]]. The M'pacha Airfield, today Katima Mulilo Airport, was constructed in 1965 at a cost of 65 million [[Finance:South African rand|Rand]], an astronomical amount at that time when 2 Rand roughly equalled 1 [[Finance:Pound sterling|Pound sterling]]. A police station was erected in 1961.<ref name=growth>{{cite news | ||
| Line 231: | Line 228: | ||
===People=== | ===People=== | ||
The Lozi people are a Bantu-speaking [[Social:Ethnicity|ethnic group]] native to [[Place:Southern Africa|southern Africa]]. They consist of several tribes, including the Bafwe, Bambukushu, Basubia, Batotela, and Bayeyi, each with its own dialect and traditional authority. These tribes share the same Lozi culture and traditions. Silozi serves as the standard language that unifies them and is widely used in educational materials, media such as television and radio, and government communications. Additionally, Silozi plays a crucial role in preserving and promoting cultural heritage, serving as a common medium for cultural practices and ceremonies. | |||
Additionally, there is a population of San, specifically the Khwe people, residing in Bwabwata in the western part of the region.<ref name=ElectionWatch/><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.ethnologue.com/language/loz|title=Lozi|website=Ethnologue|url-access=subscription}}</ref> The town's coat of arms, still very similar to that used by the Caprivi government, depicts these tribes as two elephants facing each other, symbolising unity and peaceful coexistence of the [[Social:Tribal chief|tribal chief]]s.<ref name="growth" /> | |||
===Climate=== | ===Climate=== | ||
| Line 298: | Line 297: | ||
==Politics== | ==Politics== | ||
Katima Mulilo is governed by a town council that has seven seats.<ref>{{Cite news | title=Know Your Local Authority | publisher=Institute for Public Policy Research | newspaper=Election Watch | year = 2015 | issue=3 | page=4}}</ref> | Katima Mulilo is governed by a town council that has seven seats.<ref name=ElectionWatch>{{Cite news | title=Know Your Local Authority | publisher=Institute for Public Policy Research | newspaper=Election Watch | year = 2015 | issue=3 | page=4}}</ref> | ||
Zambezi Region, whose administrative capital Katima Mulilo is, is a stronghold of Namibia's ruling SWAPO party. It won the 2010 local authority election with 2,197 votes, followed by the Rally for Democracy and Progress (RDP) with 473 votes.<ref>{{Cite web | title=Press Release Local Authority – Caprivi – Katima Mulilo | publisher=Electoral Commission of Namibia | url=http://www.ecn.na/documents/27857/181133/Press_Release_Local_Authority_-_Caprivi+-+Katima+Mulilo.pdf/1098171a-f7f1-4071-9718-a9fe5bf47cd2?version=1.0 | access-date=24 January 2018 | archive-date=25 January 2018 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180125083038/http://www.ecn.na/documents/27857/181133/Press_Release_Local_Authority_-_Caprivi+-+Katima+Mulilo.pdf/1098171a-f7f1-4071-9718-a9fe5bf47cd2?version=1.0 | url-status=dead }}</ref> SWAPO also won the 2015 local authority election by a landslide, gaining six seats and 1,875 votes. The remaining seat went to the Democratic Turnhalle Alliance (DTA) which gained 163 votes.<ref>{{cite web | title=Local elections results | publisher=Electoral Commission of Namibia | page=7 | url=http://www.ecn.na/documents/27857/218731/LA+results+%28press+release%29+2015.pdf/870a030b-8547-487f-ad18-b22713b16d4c?version=1.0 | date=28 November 2015 | access-date=7 October 2017 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151210194328/http://www.ecn.na/documents/27857/218731/LA+results+%28press+release%29+2015.pdf/870a030b-8547-487f-ad18-b22713b16d4c?version=1.0 | archive-date=10 December 2015 | url-status=dead}}</ref> | Zambezi Region, whose administrative capital Katima Mulilo is, is a stronghold of Namibia's ruling SWAPO party. It won the 2010 local authority election with 2,197 votes, followed by the Rally for Democracy and Progress (RDP) with 473 votes.<ref>{{Cite web | title=Press Release Local Authority – Caprivi – Katima Mulilo | publisher=Electoral Commission of Namibia | url=http://www.ecn.na/documents/27857/181133/Press_Release_Local_Authority_-_Caprivi+-+Katima+Mulilo.pdf/1098171a-f7f1-4071-9718-a9fe5bf47cd2?version=1.0 | access-date=24 January 2018 | archive-date=25 January 2018 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180125083038/http://www.ecn.na/documents/27857/181133/Press_Release_Local_Authority_-_Caprivi+-+Katima+Mulilo.pdf/1098171a-f7f1-4071-9718-a9fe5bf47cd2?version=1.0 | url-status=dead }}</ref> SWAPO also won the 2015 local authority election by a landslide, gaining six seats and 1,875 votes. The remaining seat went to the Democratic Turnhalle Alliance (DTA) which gained 163 votes.<ref>{{cite web | title=Local elections results | publisher=Electoral Commission of Namibia | page=7 | url=http://www.ecn.na/documents/27857/218731/LA+results+%28press+release%29+2015.pdf/870a030b-8547-487f-ad18-b22713b16d4c?version=1.0 | date=28 November 2015 | access-date=7 October 2017 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151210194328/http://www.ecn.na/documents/27857/218731/LA+results+%28press+release%29+2015.pdf/870a030b-8547-487f-ad18-b22713b16d4c?version=1.0 | archive-date=10 December 2015 | url-status=dead}}</ref> | ||
| Line 329: | Line 328: | ||
*Kenneth Matengu, Vice Chancellor of the [[Organization:University of Namibia|University of Namibia]]. | *Kenneth Matengu, Vice Chancellor of the [[Organization:University of Namibia|University of Namibia]]. | ||
*Beatrice Masilingi, athlete, 2020 Olympics 200m finalist | *Beatrice Masilingi, athlete, 2020 Olympics 200m finalist | ||
*Lorna Mabuku, professional model.<ref>http://monochromemagazine.net/2017/11/22/model-update-lorna-mabuku/</ref> | *Lorna Mabuku, professional model.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://monochromemagazine.net/2017/11/22/model-update-lorna-mabuku/ | title=Model Update: Lorna Mabuku – Monochrome Magazine | date=21 May 2022 }}</ref> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 16:23, 8 June 2025
Katima Mulilo | |
|---|---|
Town | |
 Zambezi River | |
| Nickname(s): Ngweze | |
| Motto(s): Luyeme Hamoho (Together we stand) | |
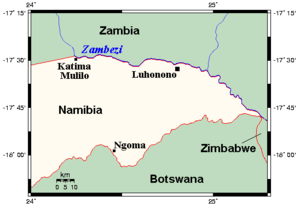 Katima Mulilo and Luhonono | |
| Coordinates: [ ⚑ ] : 17°30′14″S 24°16′30″E / 17.50389°S 24.275°E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Zambezi Region |
| Constituency | Katima Mulilo Urban |
| Founded | 1935 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Town Council |
| • Mayor | John Ntemwa |
| Area | |
| • Total | 44.9 km2 (17.3 sq mi) |
| • Land | 44.9 km2 (17.3 sq mi) |
| • Water | 0 km2 (0 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 950 m (3,120 ft) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 46,401 |
| • Density | 1,033/km2 (2,680/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (CAT) |
| Postal code | 20002 |
| Area code(s) | 066 |
| Climate | BSh |
| Website | kmtc |
Katima Mulilo or simply Katima is the capital of the Zambezi Region in Namibia. It had 46,401 inhabitants in 2023,[3][4] and comprises two electoral constituencies, Katima Mulilo Rural and Katima Mulilo Urban. It is located on the B8 national road on the banks of the Zambezi River in the Caprivi Strip in lush riverine vegetation with tropical birds and monkeys.[5] The town receives annual average rainfall of 654 millimetres (25.7 in).[6]
The nearest Namibian town to Katima Mulilo is Rundu, about 500 km away. About 40 km east of Katima Mulilo lies the village of Bukalo, where the road to Ngoma branches off and joins Namibia to Botswana.
Economy and infrastructure
Established and run as a garrison for a long time, Katima Mulilo still shows signs of its military past. In the city centre was the South African Defence Force military base and almost every house had a bomb shelter. The town benefited from the military presence in terms of infrastructure and employment, and there are still a number of military bases surrounding the town.[7]
Since the opening of the Katima Mulilo Bridge that spans the Zambezi River and connects the Zambian Copperbelt with the Namibian deep sea harbour at Walvis Bay in 2004, Katima Mulilo has become a boom town that attracts significant investment. This development has, however, also fanned illegal business activities, and driven the establishment of shanty towns to an extent that endangers social stability.[8]
The town features an Export Processing Zone and the largest open market in Namibia. There is an important international electricity inter–link facility, the Caprivi Link Inter–Connector; its inauguration has improved the power supply to the town. The Zambezi Waterfront Tourism project is (As of 2010) under construction.[7] The Caprivi Vision, a newspaper from and for the Caprivi, is published in town.[9]
Since being proclaimed a town on 2 October 1999, development has been steady but Katima Mulilo does not yet compare to more established towns and cities in Namibia. Few streets are tarred, and there is a lack of street lights and sewerage. Many residents use the bushes for lack of toilet facilities, and there have been many outbreaks of diseases such as diarrhea.[10]
The town has been affected by corruption, financial mismanagement, and infighting between councillors. Water supply has been unstable because of debt to the national water supplier, NamWater.[11]
Transport

Katima Mulilo is the terminal town of the Trans–Caprivi Highway, and the highway together with its extension to Zambia is called the Trans-Caprivi Corridor. The Trans–Caprivi Highway was opened in 1999, and the bridge to Sesheke, and with it the entire Trans-Caprivi Corridor, in 2004.[12]
Katima Mulilo is not yet connected to the Namibian railway network. In October 2007, a proposal was announced for a railway connection between Namibia and Zambia which would pass through the town.[13] The line would join Grootfontein to Katima Mulilo, then run for 130 km to Mulobezi with an 80 km upgrade of the line to Livingstone.
The town is served by Katima Mulilo Airport, situated about 18 km to the southwest, which is serviced by regular flights from the capital Windhoek.[5]
History
The name Katima Mulilo comes from the SiLozi for quench the fire, referring to nearby rapids in the Zambezi).[14] From early days (and before the advent of fire-lighting matches), there was river transport by barge (propelled by paddlers) along the Zambezi from Livingstone to Sesheke,[15] onwards past the Ngonye Falls at Sioma, where an attempt was made in about 1905 to bypass the Falls with a canal.[16] Barges were unloaded and dragged by oxen round the Falls. The route continued to Mongu, the administrative capital of Barotseland, and northwards to the settlement of Balovale (now Zambezi) in the North West of Zambia, at [ ⚑ ] 13°33′04″S 23°06′54″E / 13.551°S 23.115°E. When the barge reached Katima Mulilo, the fire was extinguished (but embers kept), and the barge was unloaded and then dragged empty up the rapids, and re-loaded before continuing the journey – but not before the fire was re-lit.[citation needed]
On 28 January 1935, the administrative centre of the Caprivi Strip was moved from Schuckmannsburg to Katima Mulilo. This date is assumed as the foundation date of Katima Mulilo. The regional office, the only brick-and-mortar building at Katima Mulilo at a time when the area consisted exclusively of pristine forests, was built under a giant Baobab situated near today's SWAPO Party regional offices. In present times the tree is known as the Toilet Tree because of a rest room carved into it.[17]
Katima Mulilo was very sparsely populated at that time. It had a missionary school run by the Seventh-day Adventists, and the small settlements were connected only by sleigh tracks. Without any roads nor other infrastructure it was difficult to administer the Caprivi Strip from here. The South African administration therefore decided to shift the regional office again, this time to Pretoria, in 1939. Given its proximity to important transport routes, particularly the railway bridge at Victoria Falls, the location of Katima Mulilo became strategically important in the Second World War which broke out soon afterwards. All military supplies, people, and goods had to be flown in. The town's first car arrived in 1940 and belonged to the air strip operator.[17]
In 1940, William "Bill" Finaughty established the first shop in the Caprivi Strip in Katima Mulilo; the settlement that surrounded the shop was subsequently named after him. In the 1950s transport on the Zambezi River was established and allowed connection to the train service at Livingstone. The M'pacha Airfield, today Katima Mulilo Airport, was constructed in 1965 at a cost of 65 million Rand, an astronomical amount at that time when 2 Rand roughly equalled 1 Pound sterling. A police station was erected in 1961.[18]
Katima Mulilo became a segregated town in 1965 when the erection of the Nghweeze township began. The South African administration was unhappy with the Mafulo informal settlement where members of the Caprivi African National Union (CANU) were staying and conducting political activism. As a response to this development, Nghweeze (derived from totela language:which literally means "stab me") township was established to enable some degree of control over Blacks by only allowing local workers and their families to take up residence. At the same time the central parts of Katima Mulilo were declared the Katima Mulilo Proper residential area and restricted to Whites. Contract workers from the company Lewis Construction from Salisbury (today's Harare) in Southern Rhodesia (today's Zimbabwe) that built Nghweeze camped in an area that for this heritage is named the Lewis informal settlement. The town had only 575 inhabitants at that time but grew to over 5,000 by 1978.[18]
In 1971 the area around Katima Mulilo got involved in the South African Border War. As in World War II, it was a strategically important location, this time due to troop transports into and out of Zambia and Angola.[19]
The settlement also was at the centre of the Caprivi conflict in the 1990s, an armed conflict between the Caprivi Liberation Army (CLA), a rebel group working for the secession of the Caprivi Strip, and the Namibian government.[20] In the early hours of 2 August 1999, CLA launched an attack occupying the state-run radio station and attacking a police station, the Wenela border post, and an army base. A state of emergency was declared in the province, and the government arrested alleged CLA supporters.[21]
Geography
Suburbs
The oldest suburbs are Nghweeze, the former Blacks' township, and Katima Mulilo Proper, the area restricted to Whites during the apartheid era. Butterfly, Cowboy, Choto and Mahohoma are registered informal settlements of Katima, further parts of town are named Nambweza, Soweto (South–Western Townships, a reminiscence of the famous suburb of Johannesburg), New Look, Mabuluma, Lyambai, Bebi, Greenwell Matongo, Macaravan East and West, and NHE (from National Housing Enterprises, a governmental low-cost housing company that drew development here).[4][22]
People
The Lozi people are a Bantu-speaking ethnic group native to southern Africa. They consist of several tribes, including the Bafwe, Bambukushu, Basubia, Batotela, and Bayeyi, each with its own dialect and traditional authority. These tribes share the same Lozi culture and traditions. Silozi serves as the standard language that unifies them and is widely used in educational materials, media such as television and radio, and government communications. Additionally, Silozi plays a crucial role in preserving and promoting cultural heritage, serving as a common medium for cultural practices and ceremonies.
Additionally, there is a population of San, specifically the Khwe people, residing in Bwabwata in the western part of the region.[23][24] The town's coat of arms, still very similar to that used by the Caprivi government, depicts these tribes as two elephants facing each other, symbolising unity and peaceful coexistence of the tribal chiefs.[18]
Climate
Katima Mulilo has a hot semi-arid climate (Köppen BSh), bordering on a dry-winter humid subtropical climate (Cwa). Almost all rainfall occurs from November to March, when the weather is hot and humid although substantially moderated by altitude. In the long dry season between April and October the weather remains hot although less humid at the beginning and finish, but very warm weather with chilly mornings occurs at the middle of this dry season during the Southern Hemisphere winter. Script error: No such module "weather box".
Politics
Katima Mulilo is governed by a town council that has seven seats.[23]
Zambezi Region, whose administrative capital Katima Mulilo is, is a stronghold of Namibia's ruling SWAPO party. It won the 2010 local authority election with 2,197 votes, followed by the Rally for Democracy and Progress (RDP) with 473 votes.[25] SWAPO also won the 2015 local authority election by a landslide, gaining six seats and 1,875 votes. The remaining seat went to the Democratic Turnhalle Alliance (DTA) which gained 163 votes.[26]
SWAPO also won the 2020 local authority election. It obtained 1,530 votes and gained four seats and the majority in the town council. One seat each went to the Popular Democratic Movement (PDM, the new name of the DTA), the Independent Patriots for Change (IPC, an opposition party formed in August 2020) and to the National Democratic Party (NDP), which came in at 448, 252, and 147 votes, respectively.[27]
Culture and education
Before Katima Mulilo was officially founded missionaries already ran schools in the area. The Seventh–day Adventists operated one, as did the Capuchin Order.[17] Today there are a number of schools in Katima Mulilo such as Katima High School, Caprivi Secondary School, Kizito Secondary School, Ngweze Secondary School, Mavuluma Secondary School and many primary and junior secondary schools.[28]
Katima Mulilo has two institutes of tertiary education, the Zambezi Vocational Center and a campus of the University of Namibia (UNAM) for teacher training, formerly the Caprivi College of Education (CCE). At the time of the merger with UNAM, CCE had 400 enrolled students and 70 staff.[29]
The town houses the community-based Caprivi Art Centre and holds an annual Caprivi Cultural Festival.[5]
Notable people
- Ryan Nyambe (born 1997), professional footballer.
- Kenneth Matengu, Vice Chancellor of the University of Namibia.
- Beatrice Masilingi, athlete, 2020 Olympics 200m finalist
- Lorna Mabuku, professional model.[30]
References
- ↑ "Table 4.2.2 Urban population by Census years (2001 and 2011)". Namibia 2011 – Population and Housing Census Main Report. Namibia Statistics Agency. p. 39. http://cms.my.na/assets/documents/p19dmn58guram30ttun89rdrp1.pdf.
- ↑ "2023 Population & Housing Census Preliminary Report". https://nsa.nsa.org.na/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Preliminary-Report-doc-fn.pdf.
- ↑ "Namibia: Regions, Towns, Villages & Settlements - Population Statistics, Maps, Charts, Weather and Web Information". https://www.citypopulation.de/en/namibia/cities/.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Inambao, Chrispin (December 2010). "Businesses mushroom". New Era.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "Katima Mulilo". The Cardboard Box. http://www.namibian.org/travel/namibia/katima_mulilo.html.
- ↑ Menges, Werner (26 May 2011). "Rainy season was one for the record books". The Namibian. http://www.namibian.com.na/news/full-story/archive/2011/may/article/rainy-season-was-one-for-the-record-books/.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Inambao, Chrispin (December 2010). "Katima owes its growth to SADF". New Era.
- ↑ Zeller, Wolfgang (March 2009). "Danger and Opportunity in Katima Mulilo: A Namibian Border Boomtown at Transnational Crossroads". Journal of Southern African Studies (Institute of Development Studies, University of Helsinki) 35 (1): 133–154. doi:10.1080/03057070802685619. https://www.pure.ed.ac.uk/ws/files/12644633/Danger_and_Opportunity_in_Katima_Mulilo.pdf.
- ↑ "About us". The Caprivi Vision. http://www.thecaprivi.com/aboutus.php.
- ↑ "Town Council Dismisses in vote buying bid?". The Caprivi Vision. n.d.. http://www.caprivivision.com/article.php?articleID=sdwmaiiv.
- ↑ Dentlinger, Lindsay (12 May 2004). "Towns face chance for change". The Namibian. http://www.namibian.com.na/index.php?id=28&tx_ttnews%5Btt_news%5D=9202&no_cache=1.
- ↑ "Trans–Caprivi Corridor". Walvis Bay Corridor Group. http://www.wbcg.com.na/corridors/trans-caprivi-corridor.html.
- ↑ Railways Africa – NEW NAMIBIAN EXTENSION
- ↑ "Katima Mulilo". Namibia 1on1. http://www.namibia-1on1.com/katima-mulilo.html.
- ↑ "Betty Clay | 1936 - 1939 Newly-wed". http://www.spanglefish.com/BettyClay/index.asp?pageid=638516.
- ↑ MacMillan, Hugh; Hugh, Macmillan (27 May 2005). An African Trading Empire: The Story of Susman Brothers & Wulfsohn, 1901–2005. Bloomsbury Academic. ISBN 9781850438533. https://books.google.com/books?id=KWh2S2d68XoC&pg=PA52.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 Inambao, Chrispin (December 2010). "A historical perspective—from rural backwater to vibrant town". New Era.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 Inambao, Chrispin (December 2010). "Rapid growth to urban centre". New Era.
- ↑ Matjila, Andrew N (December 2010). "Down memory lane". New Era.
- ↑ "Caprivi Liberation Front". fas.org. http://fas.org/irp/world/para/caprivi.htm.
- ↑ "Civil supremacy of the military in Namibia: A retrospective case study". NamibWeb. http://namibweb.com/article2.htm.
- ↑ Sanzila, George (25 June 2013). "Taps and sewerage for Chotto and others". New Era. http://www.newera.com.na/articles/52657/Taps-and-sewerage-for-Chotto-and-others.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 "Know Your Local Authority". Election Watch (Institute for Public Policy Research) (3): p. 4. 2015.
- ↑ "Lozi". https://www.ethnologue.com/language/loz.
- ↑ "Press Release Local Authority – Caprivi – Katima Mulilo". Electoral Commission of Namibia. http://www.ecn.na/documents/27857/181133/Press_Release_Local_Authority_-_Caprivi+-+Katima+Mulilo.pdf/1098171a-f7f1-4071-9718-a9fe5bf47cd2?version=1.0.
- ↑ "Local elections results". Electoral Commission of Namibia. 28 November 2015. p. 7. http://www.ecn.na/documents/27857/218731/LA+results+%28press+release%29+2015.pdf/870a030b-8547-487f-ad18-b22713b16d4c?version=1.0.
- ↑ "Publication of results and particulars in respect of general elections for local authority councils: Electoral Act, 2014". Government Gazette of the Republic of Namibia (Government of Namibia) (7497): p. 21. 1 April 2021. https://www.ecn.na/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/7497-Gov-N65-Results-LA-2020.pdf.
- ↑ "Caprivi Schools". Association of Regional Councils in Namibia. http://www.arc.org.na/home.php?pn=caprivi_schools.
- ↑ Magadza, Moses (9 May 2010). "Namibia: Teacher colleges merge with university". University World News. http://www.universityworldnews.com/article.php?story=20100507211902877.
- ↑ "Model Update: Lorna Mabuku – Monochrome Magazine". 21 May 2022. http://monochromemagazine.net/2017/11/22/model-update-lorna-mabuku/.
 |