Engineering:Fiber pushout test
From HandWiki
Revision as of 23:54, 8 July 2022 by imported>John Stpola (update)
The fiber pushout test is a mechanical test performed on composite materials where a fiber is mechanically pushed out of the material. This test is carried out with the purpose of measuring the matrix/fiber interface de-bonding energy and the effects of frictional sliding between the matrix and the fiber.
To perform this test flat indentation tips, usually made of diamond or tungsten, are used. These tips are mechanically lowered onto the location of the fiber on the composite using a CCD
This test is not to be confused with fiber pull-out, which is a composite crack propagation phenomenon.
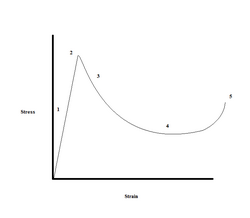
- The mechanics behind the test are as follows:
- 1. Elastic loading
- The flat tip indenter is lowered onto the fiber using a CCD camera to guide the indenter downwards
- 2. Progressive de-bonding
- The indenter touches the fiber and begins applying load, bonds begin to break between the matrix and the fiber
- 3. Fiber push through
- The bonds between the matrix and fiber are totally broken and the fiber begins to slide out of the matrix
- 4. Interfacial sliding
- the indenter continues to push the fiber through the matrix, the only force resisting this movement is frictional
- 5. Indenter matrix collision
- The fiber has been totally pushed out of the matrix and the indenter collides with the matrix surface. This gives the total displacement of the fiber.
References
- Mechanical Behavior of Materials,(2009) Cambridge University Press by M.A. Meyers and K.K. Chawlars, Second Edition, Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, 1999
External links