Biology:Supercompensation
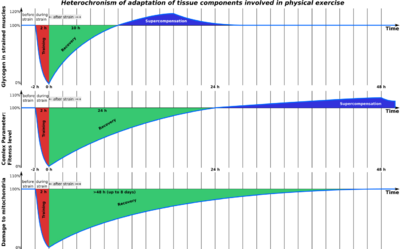
In sports science theory, supercompensation is the post training period during which the trained function/parameter has a higher performance capacity than it did prior to the training period.[1]
Description
The fitness level of a human body in training can be broken down into four periods: initial fitness, training, recovery, and supercompensation. During the initial fitness period, the target of the training has a base level of fitness (shown by the first time sector in the graph). Upon entering the training period, the target's level of fitness decreases (shown by the second time sector in the graph). After training, the body enters the recovery period during which level of fitness increases up to the initial fitness level (shown by the third time sector in the graph). Because the human body is an adjustable organism, it will feel the need to adjust itself to a higher level of fitness in anticipation of the next training session. Accordingly, the increase in fitness following a training session does not stop at the initial fitness level. Instead the body enters a period of supercompensation during which fitness surpasses the initial fitness level (shown by the fourth time sector in the graph). If there are no further workouts, this fitness level will slowly decline back towards the initial fitness level (shown by the last time sector in the graph). First put forth by Russian scientist Nikolai N. Yakovlev (1911–1992) in 1949–1959,[2] this theory is a basic principle of athletic training.
If the next workout takes place during the recovery period, overtraining may occur. If the next workout takes place during the supercompensation period, the body will advance to a higher level of fitness. If the next workout takes place after the supercompensation period, the body will remain at the base level.
More complex variations are possible; for instance, sometimes a few workouts are intentionally made in the recovery period to achieve greater supercompensation effects.[3]
The relation between supercompensation and training programs
At a first glance, creating effective training programs might look simple. All you need is to determine the intensity level and how long it takes you to get to the supercompensation period. Afterwards, continue training with the intensity level that was determined previously and keep the necessary intervals between workouts required for supercompensation. However, things become more complex because training affects many different bodily functions and parameters. Each bodily function or parameter has a different recovery time, a different amount of time needed to reach peak supercompensation, a different amount of time between supercompensation peak and return to base fitness.
The aforementioned functions and parameters are basic ones. Muscle strength and mass are complex parameters. For instance, muscle mass is a function of many different simple parameters. For example, amount of glycogen in muscles is a basic parameter that influences muscle mass.
Use of supercompensation in practice
In classical sport science, the yearly (sometimes multi-yearly) period is divided to micro and macro cycles, where each microcycle is responsible for the development of a specific (sometimes several) basic training function and parameter, whereas macrocycles are responsible for the development of complex parameters/functions (such as muscle strength). During each microcycle, the resting period is the same as the amount of time needed for reaching the supercompensation stage of the current training parameter/function (also during such a micro cycle there shouldn't be any negative influence on the recovery of the main function). Such a training method will work only when the developed functions/parameters are non-related. Unfortunately, for muscle strength and mass this is not the case (functions/parameters are related). Therefore, for muscle strength and mass different approaches are needed. During a training cycle the intensity and volume of training varies, waves of different functions are overlaid so that until the end of the microcycle supercompensation of the main required functions is achieved.
References
- ↑ "Defining supercompensation training". March 9, 2009. http://www.humankinetics.com/excerpts/excerpts/defining-supercompensation-training.
- ↑ Viru, Atko (April 17, 2002). "Early contributions of Russian stress and exercise physiologists". Journal of Applied Physiology 92 (4): 1378–1382. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00435.2001. PMID 11896000.
- ↑ Marrier, Bruno; Robineau, Julien; Piscione, Julien; Lacome, Mathieu; Peeters, Alexis; Hausswirth, Christophe; Morin, Jean-Benoît; Meur, Yann Le (2017-01-25). "Supercompensation Kinetics of Physical Qualities During a Taper in Team Sport Athletes". International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance 12 (9): 1163–1169. doi:10.1123/ijspp.2016-0607. ISSN 1555-0265. PMID 28121198.
External links
- Shea, Jason. "Fatigue, Recovery, and Supercompensation". http://www.teamunify.com/cseksc/__doc__/Shea_FatigueRecoverySupercompensation-2.pdf.
- Bompa, Tudor O.; Haff, Greg (10 August 2009). Periodization: theory and methodology of training. Human Kinetics. pp. 18–. ISBN 978-0-7360-8547-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=09mT_sJ6KxoC&pg=PA18. Retrieved 30 September 2011.
- Janssen, Peter G. J. M. (2001). Lactate threshold training. Human Kinetics. pp. 151–. ISBN 978-0-7360-3755-6. https://archive.org/details/lactatethreshold00jans. Retrieved 30 September 2011.
- Fee, Earl W. (30 April 2005). The Complete Guide To Running: How To Be A Champion From 9 To 90. Meyer & Meyer Verlag. pp. 119–. ISBN 978-1-84126-162-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=kviGin1ahRoC&pg=PA119. Retrieved 30 September 2011.


