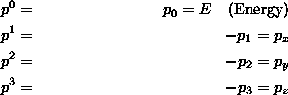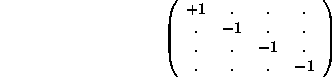Physics:Four-momenta
Energy and vector momenta of a particle or set of particles can be combined into a four(dimensional)-vector p. The components are
where ![]() and pz are the momentum components along a system of orthogonal axes. Then if the particle has mass m,
and pz are the momentum components along a system of orthogonal axes. Then if the particle has mass m,
Using the convention of summing over repeated indices, this last line can be written as
where ![]() is a tensor, the metric tensor of the Minkovski or Lorentz geometry
is a tensor, the metric tensor of the Minkovski or Lorentz geometry
in which dots indicate zeros. ![]() with an upper index is called a contravariant four-vector, while
with an upper index is called a contravariant four-vector, while ![]() with a lower index is covariant; the relation is that
with a lower index is covariant; the relation is that ![]() .
.
The principles of conservation of linear momentum and of energy together give conservation of four-momentum, in any elementary particle interaction or decay. For any system of particles an effective mass can be defined
where ![]() is the total four-momentum. The effective mass is a relativistic invariant and is conserved in any interaction. Thus if a particle of mass M decays into several other particles, their effective mass will be M.
is the total four-momentum. The effective mass is a relativistic invariant and is conserved in any interaction. Thus if a particle of mass M decays into several other particles, their effective mass will be M.
The scalar product of any pair of four-vectors is defined by