Engineering:M Scow
 Class symbol | |
 | |
| Development | |
|---|---|
| Designer | Johnson/Melges Boat Works |
| Location | United States |
| Year | 1950 |
| Builder(s) | Tanzer Industries Melges Performance Sailboats Windward Boatworks |
| Role | One-design racer |
| Boat | |
| Boat weight | 440 lb (200 kg) |
| Draft | 2.67 ft (0.81 m), with a bilgeboard down |
| Hull | |
| Type | Monohull |
| Construction | Fiberglass |
| LOA | 16.00 ft (4.88 m) |
| Beam | 5.80 ft (1.77 m) |
| Hull appendages | |
| Keel/board type | twin bilgeboards |
| Rudder(s) | dual internally-mounted rudders |
| Rig | |
| Rig type | Bermuda rig |
| Sails | |
| Sailplan | Fractional rigged sloop |
| Mainsail area | 108.00 sq ft (10.034 m2) |
| Jib/genoa area | 39.00 sq ft (3.623 m2) |
| Total sail area | 147.00 sq ft (13.657 m2) |
| Racing | |
| D-PN | 89.3 |
The M Scow, also called the M-Scow and the M-16 Scow, is a Canada /United States sailing dinghy that was designed by Johnson Boat Works and Melges Boat Works as a one-design racer and first built in 1950.[1][2]
Production
The design was built by Tanzer Industries in Dorion, Quebec, Canada as well as by Windward Boatworks in Middleton, Wisconsin United States and Melges Performance Sailboats in Zenda, Wisconsin, also in the United States, but it is now out of production.[1][2][3][4][5]
Design
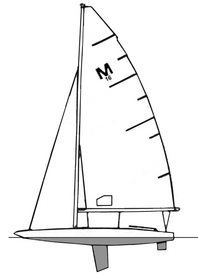
The M Scow is a recreational sailboat, built predominantly of fiberglass, with wood trim. It has a fractional sloop rig with tapered or untapered aluminum or wooden spars. The hull is a reverse sheer scow design, with dual internally-mounted rudders controlled by a tiller and a dual retractable bilgeboards. It displaces 440 lb (200 kg).[1][2]
The boat has a draft of 2.67 ft (0.81 m) with a bilgeboard extended. It can be transported on a trailer.[1]
For sailing the design was originally equipped with end-boom sheeting to a mainsheet traveler, mainsail and jib windows for improved visibility. It also has a boom vang and Cunningham, barber haulers, and a jib traveler.[2]
The dual rudders, rotating mast and the mainsheet traveler were done away with in a 1999 redesign. The hull and rigging were also changed to the MC Scow hull and rigging designs. In the 2020 the MC Scow remained in production, while the M Scow was no longer offered for sale.[1][6][7]
The design has a Portsmouth Yardstick racing average handicap of 89.3 and is normally raced with a crew of two sailors.[2]
Operational history
In a 1994 review Richard Sherwood wrote, "the M-16 scow is raced on the East Coast, in the Southeast, and in the Southwest, but most boats are found in the Midwest ... limiting specifications are issued by the Inland Lake Yachting Association, which holds a championship regatta with 60 to 90 competitors."[2]
See also
Similar boats
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 McArthur, Bruce (2020). "M-16 Scow sailboat". sailboatdata.com. https://sailboatdata.com/sailboat/m-16-scow.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Sherwood, Richard M.: A Field Guide to Sailboats of North America, Second Edition, pages 70-71. Houghton Mifflin Company, 1994. ISBN:0-395-65239-1
- ↑ McArthur, Bruce (2020). "Melges Performance Sailboats". sailboatdata.com. https://sailboatdata.com/builder/melges-performance-sailboats.
- ↑ McArthur, Bruce (2020). "Tanzer Industries Ltd. 1966 - 1986". sailboatdata.com. https://sailboatdata.com/builder/tanzer-industries-ltd.
- ↑ McArthur, Bruce (2020). "Windward Boatworks". sailboatdata.com. https://sailboatdata.com/builder/windward-boatworks.
- ↑ McArthur, Bruce (2020). "MC Scow sailboat specifications and details". sailboatdata.com. https://sailboatdata.com/sailboat/mc-scow.
- ↑ Melges Performance Sailboats (2020). "The Melges MC Scow". melges.com. https://melges.com/melges-mc/.
External links
 |

