Medicine:Nuclear groove
From HandWiki
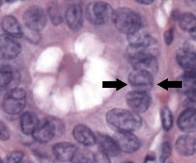
A nuclear groove is an invagination of the nuclear envelope, in the longitudinal axis.[1] It can be present in:
- Thyroid neoplasms: It is a characteristic feature of papillary thyroid carcinoma, but has also been seen in other types of thyroid neoplasms, as well as in non-neoplastic thyroid lesions.[1]
- Ovarian tumors including Brenner tumors, adult granulosa cell tumors, and transitional cell tumors.[1]
- Breast carcinomas[1]
- Vaginal, cervical and/or endometrial neoplasms
- Papillary neoplasms of several organs: papillary transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder, papillary renal cell carcinoma, papillary endometrioid carcinoma of the prostate, in thymic carcinomas, and in non-epithelial tumors.
References
 |