Medicine:Dual Source CT
| Dual source CT | |
|---|---|
 Dual source diagram | |
| Other names | Dual source computed tomography |
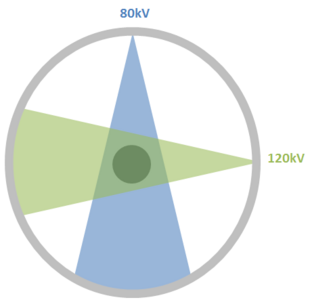
Dual Source CT is a specific form of computed tomography (CT) which contains two x-ray tubes and corresponding detectors to generate internal images of an object.[1]
Mechanism
The Dual Source CT has two sources which are used simultaneously for scanning to create internal pictures. Since the acquisition is simultaneous, the time for the scanning is reduced.[2]
History
Dual Source CT scanners were introduced in 2005.
Advantages
Dual source Ct scanner allow fast scanning with higher temporal resolution by acquiring a full CT slice in only half a rotation. Fast imaging reduces motion blurring at high heart rates and potentially allowing for shorter breath-hold time. This is particularly useful for ill patients having difficulty holding their breath or unable to take heart-rate lowering medication.[2][3]
References
- ↑ Carrascosa, Patricia M.; Cury, Ricardo C.; García, Mario J.; Leipsic, Jonathon A. (2015-10-03) (in en). Dual-Energy CT in Cardiovascular Imaging. Springer. pp. 12. ISBN 978-3-319-21227-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=wJ2oCgAAQBAJ&q=dual+source+ct.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Seidensticker, Peter R.; Hofmann, Lars K. (2008-05-24) (in en). Dual Source CT Imaging. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-3-540-77602-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=oUtHea3ZnJ0C&q=dual+source+ct.
- ↑ Schmidt, Bernhard; Flohr, Thomas (2020-11-01). "Principles and applications of dual source CT" (in English). Physica Medica: European Journal of Medical Physics 79: 36–46. doi:10.1016/j.ejmp.2020.10.014. ISSN 1120-1797. PMID 33115699. https://www.physicamedica.com/article/S1120-1797(20)30257-X/abstract.

