Biology:Spathoglottis paulinae
| Small purple orchid | |
|---|---|
| |
| Illustration by Lewis Roberts | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Order: | Asparagales |
| Family: | Orchidaceae |
| Subfamily: | Epidendroideae |
| Genus: | Spathoglottis |
| Species: | S. paulinae
|
| Binomial name | |
| Spathoglottis paulinae F.Muell.[1]
| |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
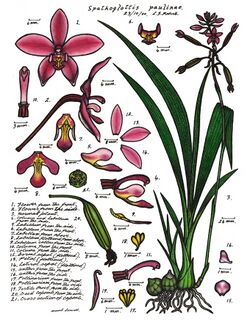
Spathoglottis paulinae, commonly known as the small purple orchid,[2] is a plant in the orchid family and is native to New Guinea and Tropical North Queensland. It is an evergreen terrestrial orchid with crowded pseudobulbs, between four and seven large, pleated leaves and up to thirty mauve to purple flowers.
Description
Spathoglottis paulinae is an evergreen, terrestrial herb with crowded pseudobulbs 30–50 mm (1–2 in) long and wide just below the surface of the soil. There are between four and seven dark green, pleated leaves emerging from each pseudobulb. The leaves are lance-shaped, 80–180 mm (3–7 in) long and 30–50 mm (1–2 in) wide on a stalk 60–120 mm (2–5 in) long. Between six and thirty pale mauve to purple flowers 20–30 mm (0.8–1 in) long and wide are borne on a flowering stem 30–120 mm (1–5 in) long. The sepals are 12–20 mm (0.5–0.8 in) long, 5–7 mm (0.2–0.3 in) wide and the petals are 10–18 mm (0.4–0.7 in) long, 8–9 mm (0.3–0.4 in) wide. The sepals are egg-shaped with the narrower end towards the base, the petals are broadly egg-shaped and all five make a star-like shape. The labellum projects forward, 9–12 mm (0.4–0.5 in) long, 9–10 mm (0.35–0.39 in) wide and has three lobes. The middle lobe is spatula-shaped with two yellow calli and the side lobes are narrow and curve upwards. Flowering occurs between July and March. Some plants appear to be self-pollinating with flowers that barely open whilst others are insect pollinated and open widely for a few days.[2][3][4]
Taxonomy and naming
Spathoglottis paulinae was first formally described in 1867 by Ferdinand von Mueller who published the description in Fragmenta phytographiae Australiae.[5][6]
Distribution and habitat
'The small purple orchid grows in wet places with grasses in open forest. It occurs in Papua New Guinea, West New Guinea in tropical north Queensland between Cooktown and Ingham and in northern parts of the Northern Territory.[2][3][4]
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Spathoglottis paulinae. |
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Spathoglottis paulinae". World Checklist of Selected Plant Families (WCSP). Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://wcsp.science.kew.org/namedetail.do?name_id=193274.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Jones, David L. (2006). A complete guide to native orchids of Australia including the island territories. Frenchs Forest, N.S.W.: New Holland. p. 363. ISBN 1877069124.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Factsheet - Spathoglottis paulinae". Centre for Australian National Biodiversity Research (CANBR), Australian Government. 2010. http://www.canbr.gov.au/cpbr/cd-keys/RFKOrchids/key/rfkorchids/Media/Html/Spathoglottis_paulinae.htm.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Spathoglottis paulinae". Orchids of New Guinea. http://www.orchidsnewguinea.com/orchid-information/species/speciescode/932. Retrieved 2 November 2018.
- ↑ "Spathoglottis paulinae". APNI. https://id.biodiversity.org.au/instance/apni/479042. Retrieved 26 October 2018.
- ↑ von Mueller, Ferdinand (1867). Fragmenta phytographiae Australiae (Volume 6). Melbourne: Victorian Government Printer. p. 95. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/764793#page/96/mode/1up. Retrieved 2 November 2018.
Wikidata ☰ Q5228651 entry
 |

