Biology:Hakea erecta
| Hakea erecta | |
|---|---|

| |
| Hakea erecta growing near Wongan Hills | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Proteales |
| Family: | Proteaceae |
| Genus: | Hakea |
| Species: | H. erecta
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hakea erecta Lamont[1]
| |
| |
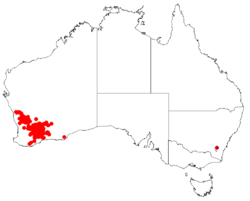
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
Hakea erecta is a shrub in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to Western Australia. It is a dense rounded shrub with linear twisted leaves and up to 24 pink or white fragrant flowers appearing in leaf axils in spring.
Description
Hakea erecta is a rounded non lignotuberous shrub which typically grows to a height of 0.5 to 2.6 metres (2 to 9 ft) and has many spreading branches and smooth grey bark. Branchlets are silky with dense flat hairs at flowering. The leaves may be either smooth or hairy, 4–10 cm (2–4 in) long and 2.5–5 mm (0.098–0.20 in) wide, linear, flat and twisted at the base and end in a sharp point. Leaves have a prominent centre vein and 3 veins on the underside. The single inflorescence has 16-24 pink-cream sweetly scented flowers in a raceme and appear in clusters in the leaf axils mostly in upper branchlets. The perianth is pink or white, pedicels are pink and smooth. The style is 6.5–8 mm (0.26–0.31 in) long. Flowering occurs from September to October. The oblong to egg-shaped fruit has a smooth surface except for a few tubercles, ending with a small pointed beak.[2][3][4][5]
Taxonomy and naming
This hakea was first formally described in 1987 by Byron Lamont from a specimen collected near Pingrup and the description was published in the Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society.[6] The specific epithet (erecta) is a Latin word meaning "upright",[7] referring to the more or less erect stems, leaves and fruit.[4]
Distribution and habitat
It is endemic to an area in the Mid West, Wheatbelt, Great Southern and Goldfields-Esperance regions of Western Australia where it grows in scrubland and low woodland on deep sandy soils often around laterite.[8]
Conservation status
Hakea erecta is classified as "not threatened" by the Western Australian Government Department of Parks and Wildlife.[8]
Use in horticulture
Hakea erecta is a frost-tolerant, long-flowering, mid-sized shrub with attractive scented blooms. It is an adaptable species, forming into dense thickets providing a good wildlife habitat and low windbreak.[2][3]
References
- ↑ "Hakea erecta". Council of Heads of Australian Herbaria. https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/search?product=APC&tree.id=51209179&name=Hakea+erecta&inc._scientific=&inc.scientific=on&inc._cultivar=&max=100&display=apc&search=true.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Young, J A. Hakeas of Western Australia:A Field and Identification Guide. ISBN 0-9585778-2-X.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Holliday, Ivan (2005). Hakeas:A Field and Garden Guide. Reed New Holland. ISBN 1-877069-14-0.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Hakea erecta". State herbarium of South Australia. http://www.flora.sa.gov.au/efsa/lucid/Hakea/key/Australian%20Hakea%20species/Media/Html/Hakea_erecta.htm.
- ↑ Wilson (ed), Annette; Barker, Robyn M.; Haegi, Laurence A.; Barker, William R. (1999). "Flora of Australia" Volume 17B Proteaceae 3 Hakeas to Dryandra. ABRS-Department of Environment & Heritage. ISBN 0-643-06454-0.
- ↑ "Hakea erecta". APNI. https://id.biodiversity.org.au/instance/apni/480073.
- ↑ Brown, Roland Wilbur (1956). The Composition of Scientific Words. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press. p. 307.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Hakea erecta". FloraBase. Western Australian Government Department of Parks and Wildlife. https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/browse/profile/2157.
Wikidata ☰ Q18079965 entry
 |


