Engineering:Hjortspring boat
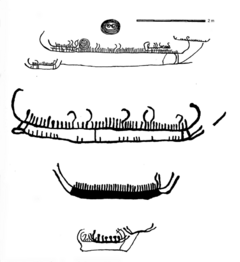
The Hjortspring boat (Danish: Hjortspringbåden) is a vessel designed as a large canoe, from the Scandinavian Pre-Roman Iron Age. It was built circa 400–300 BCE. The hull and remains were rediscovered and excavated in 1921–1922 from the bog of Hjortspring Mose on the island of Als in Sønderjylland, southern Denmark .[1] The vessel is a clinker-built wooden boat of more than 19 metres (62 feet) length overall, 13.6 metres (45 feet) long inside, and 2 metres (6.5 feet) wide. Ten thwarts fit to be seats span the boat with room for two persons each; this suggests space for a crew of at least 20 who propelled the boat with paddles. [2] The boat would have weighed an estimated 530 kilograms (1,168 pounds), making it easily portable by its crew. When found, it contained a great quantity of weapons and armour, including 131 shields of the Celtic type, 33 well-crafted shield bosses, 138 spearheads of iron, 31 spearheads of bone or antler, 11 single-edged iron swords, and the remains of several mailcoats. Two of the swords were deliberately bent, a practice associated with Iron Age rituals. The largest of the spearheads is a massive 43.5 centimetres (17 inches) long. The find also contained bowls, boxes, blacksmith's tools, and other everyday goods. The sinking of the vessel in the bog has been interpreted as a deliberate votive offering.[3] This is reinforced by the presence of a dismembered horse placed beneath the boat at the time of burial along with a lamb, a calf, and two dogs. Numerous graves have been discovered in Denmark from this time period containing similar grave goods and sacrificed horses, dogs, lambs, cows, other animals, and human beings.[4][5][6][7]
The boat is the oldest find of a wooden plank ship in Scandinavia and it closely resembles the thousands of petroglyph images of Nordic Bronze Age ships found throughout Scandinavia.[2] The Hjortspring boat was constructed of lime (linden) wood planks which were sewn together with cord of lime bark, spruce root, or rawhide. Pitch was used to caulk and coat the seams to make the boat watertight. A long dugout log forms the bottom plank which also acts as the keel with two additional planks, or strakes, attached on both sides to fashion the hull. This allows the large vessel to sit high in the water and to traverse shallow waters, even with a full crew and heavy load. Hollowed timbers were used to create the distinct stem and stern-posts. These stem pieces, along with the bottom plank, extend outward from the hull to form the iconic “beaks” of this type of boat construction. Vertical oak struts, secured by wooden pegs and resin, fasten the upper and lower “beaks” and brace both ends of the watercraft. Thin limbs of hazel form the ribs which were lashed to cleats in the planks. These cleats were made by carving down the rest of the plank boards; this created a strong attachment point without need for fastening each cleat separately by lashing or pegs to the long planks of the hull. The hull planks and hazel ribs are supported by thwarts and thicker supporting ribs of ash.
The high level of craftsmanship present in the archeological find indicates that the boat building methods used to construct the Hjortpsring boat are significantly older than the Hjortspring boat itself.[8]
Watercraft of this style and construction were built and used at least until the 3rd century CE. Metal rivets become increasing present in later finds and the stem construction was simplified to a single curved shape which extended and tapered outward from the hull. These later stems, or prows were made of single pieces of wood, or multiple pieces joined together. Much of the essential boat building methods found in the Hjortspring boat persisted to the Viking Age. This continuation can be seen in the boat finds from Halsnøy (200 CE), Nydam (300-400 CE), Sutton Hoo (600-700 CE), and Kvalsund (690 CE).[9]
See also
- Iron Age Scandinavia
- Sewn boat
- Ship burial
- Nydam Mose
- National Museum of Denmark
- Dugout canoe
- Clinker (boat building)
- Bog body
- Death in Norse paganism
References
- ↑ Nationalmuseet (Denmark); Thorkild Ramskou (1965). Danmarks oldtid. p. 43. https://books.google.com/books?id=BI0QAQAAIAAJ. Retrieved 2 July 2013.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Pauline Asingh (2009). Grauballemanden. Gyldendal A/S. pp. 195–. ISBN 978-87-02-05688-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=zZy-4znpeWIC&pg=PA195. Retrieved 2 July 2013.
- ↑ Thomas Dickson (2009). Dansk design. Gyldendal A/S. pp. 31–. ISBN 978-87-02-07768-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=OPokY4jolNwC&pg=PA31. Retrieved 2 July 2013.
- ↑ Glob, P. V. (1969). The Bog People: Iron-Age Man Preserved. Faber and Faber Ltd.. pp. 185, 186.
- ↑ Kaul, Flemming (1988). Da våbnene tav: Hjortspringfundet og dets baggrund. Copenhagen, Denmark: Danish National Museum.
- ↑ Randsborg, Klavs. (1999). Carman, John; Harding, Anthony. eds. Into the Iron Age: A Discourse on War and Society. Stroud, U.K: Sutton. pp. 191-202.
- ↑ Hjortspring: Warfare and Sacrifice in Early Europe. Århus, Denmark: Århus University Press. 1996.
- ↑ Christensen, Arne Emil (1968) (in English). Boats of the North: A History of Boatbuilding in Norway. Oslo, Norway: Det Norske Samlaget. pp. 18, 19, 20.
- ↑ Brøgger, A. W.; Shetelig, Haakon (1951). The Viking Ships: Their Ancestry and Evolution. Oslo, Norway: Dreyers Forlag. pp. 48-60.
Further reading
- Ole Crumlin-Pedersen and Athena Trakadas (eds.), Hjortspring: A Pre-Roman Iron-Age Warship in Context, [Ships and Boats of the North Volume 5], Roskilde: Viking Ship Museum 2003; 293pp; CD-ROM; ISBN:8785180521
- Brøgger, A. W.; Shetelig, Haakon, The Viking Ships: Their Ancestry and Evolution, trans. Katherine John, Oslo: Dreyers Forlag 1951
External links
- "The Guild of the Hjortspring Boat". http://www.hjortspring.dk.
- Foteviken Museum. "The Hjortspring boat". http://www.foteviken.se/sewnboat/hjortspring.html.
- "Bibliography on the boat". Southampton University. Archived from the original on 2005-01-01. https://web.archive.org/web/20050101182327/http://cma.soton.ac.uk/histship/flrf139.htm.
- "Review of Crumlin's book". University College London. http://www.ucl.ac.uk/prehistoric/reviews/04_08_crumlin.htm.
- "The conservation of the boat". Danish National Museum. Archived from the original on 2005-08-28. https://web.archive.org/web/20050828001452/http://www.natmus.dk/cons/x/ww/ww1.htm.
- Axel Nelson. "A history of pre-Viking Age Scandinavian ships (in Swedish)". http://axelnelson.com/skepp/prewiking.html.