Social:Middle Sepik languages
From HandWiki
| Middle Sepik | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | East Sepik Province, in the Sepik River basin of Papua New Guinea |
| Linguistic classification | Sepik
|
| Subdivisions |
|
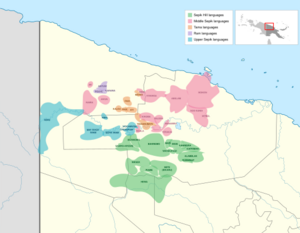 The Sepik languages as classified by Foley (2018) | |
The Middle Sepik languages comprise diverse groups of Sepik languages spoken in northern Papua New Guinea. The Middle Sepik grouping is provisionally accepted by Foley (2018) based on shared innovations in pronouns, but is split up by Glottolog. They are spoken in areas surrounding the town of Ambunti in East Sepik Province.
Unlike most other Sepik languages, Middle Sepik languages do not overtly mark gender on nouns, although the third-person singular pronoun does distinguish between masculine and feminine genders (e.g., Proto-Ndu *nd- ‘3sg.m’ and *l- ‘3sg.f’).[1]
Languages
Languages are:[1]
- Ndu languages: Gala, Manambu, Kaunga (Yelogu), Sawos, Iatmul (Nyaura), Ambulas (Abelam), Boiken
- Nukuma languages: Kwoma (Washkuk); Mende, Kwanga
- Yerakai (Garamambu)
- Yellow River languages: Namia (Namie), Ak, Awun
Pronouns
Middle Sepik pronouns:[1]:241
pronoun Manambu Kwoma Yerakai Namia 1sg wun an ana ona 2sg.m mɨn mɨ mun am 2sg.f ɲɨn ni nen ne 3sg.m ndɨ rɨ dit lo-ko 3sg.f lɨ sɨ sis e-ko 1du an si tet era 2du mbɨr ki mbot awa-pli 3du mbɨr pɨr ŋgit la-pli-ko 1pl ɲan no no-m ema 2pl ŋgwur kwo ŋgo-m wa-m 3pl ndɨy ye lal lo-m-ko
Middle Sepik pronominal innovations:[1]
- second/third person dual pronoun *(m)pri
- second person plural pronoun *(ŋ)kwV, although this could have been inherited from Proto-Sepik *ko (2PL) as well
References
- Ross, Malcolm (2005). "Pronouns as a preliminary diagnostic for grouping Papuan languages". in Andrew Pawley. Papuan pasts: cultural, linguistic and biological histories of Papuan-speaking peoples. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics. pp. 15–66. ISBN 0858835622. OCLC 67292782.

