Physics:Multifocal diffractive lens
A multifocal diffractive lens is a diffractive optical element (DOE) that allows a single incident beam to be focused simultaneously at several positions along the propagation axis.[1]
Principle of operation
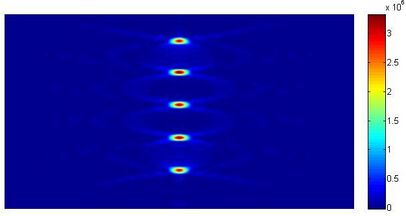
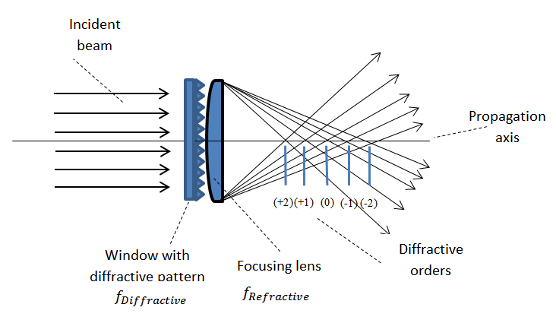
An incident laser beam is deflected by grooved diffraction pattern into axial diffraction orders along its optical axis. The foci appear around the far field position. With an additional focusing lens, foci from multifocal lens will appear at certain distances from the focal point of the lens.
Theory
The multifocal spots location is a function of refractive focal length fRefractive and predetermined diffractive focal length fDiffractive The focal spot at the "zero" order refers to the refractive focal length of the lens being used.
The distance between the focal spots can be described by the equation
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac {1}{f_m} = \frac {1}{f_\mathrm{Refractive}}+\frac{m}{f_\mathrm{Diffractive}},\ \mathrm{for}\ m = \pm 1, \pm 2, \pm 3... }[/math],
- where fm is the focal length for the mth diffractive order,
- fRefractive is the focal length of the refractive lens, and
- fDiffractive is the focal length of the diffractive lens.
Applications
- Laser cutting
- Laser drilling
- Microscopy
- Ophthalmology: Multifocal contact lenses and multifocal intraocular lenses[1]
External links
- HOLOOR Application note for Multifocal Lenses
- Interactive Optical calculator for Multifocal Lenses
- Beam Propagation through multifocal lens (Movie)
References
 |