Voronoi pole
In geometry, the positive and negative Voronoi poles of a cell in a Voronoi diagram are certain vertices of the diagram.
Definition
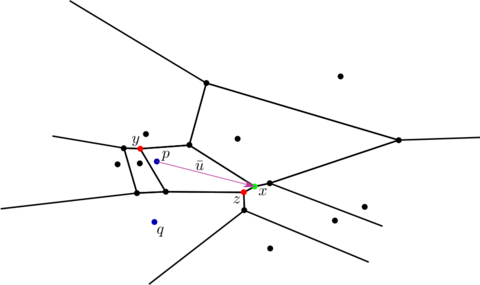
Let [math]\displaystyle{ V }[/math] be the Voronoi diagram for a set of sites [math]\displaystyle{ P }[/math], and let [math]\displaystyle{ V_p }[/math] be the Voronoi cell of [math]\displaystyle{ V }[/math] corresponding to a site [math]\displaystyle{ p\in P }[/math]. If [math]\displaystyle{ V_p }[/math] is bounded, then its positive pole is the vertex of the boundary of [math]\displaystyle{ V_p }[/math] that has maximal distance to the point [math]\displaystyle{ p }[/math]. If the cell is unbounded, then a positive pole is not defined.
Furthermore, let [math]\displaystyle{ \bar{u} }[/math] be the vector from [math]\displaystyle{ p }[/math] to the positive pole, or, if the cell is unbounded, let [math]\displaystyle{ \bar{u} }[/math] be a vector in the average direction of all unbounded Voronoi edges of the cell. The negative pole is then the Voronoi vertex [math]\displaystyle{ v }[/math] in [math]\displaystyle{ V_p }[/math] with the largest distance to [math]\displaystyle{ p }[/math] such that the vector [math]\displaystyle{ \bar{u} }[/math] and the vector from [math]\displaystyle{ p }[/math] to [math]\displaystyle{ v }[/math] make an angle larger than [math]\displaystyle{ \tfrac{\pi}{2} }[/math].
References
- Boissonnat, Jean-Daniel (2007). Effective Computational Geometry for Curves and Surfaces. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-33258-9.
 |