Software:CubePort
| Developer(s) | ExoLogic Corporation (2002-current) |
|---|---|
| Stable release | v2.23
/ 03-31-2010 |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Type | Data transformation |
| License | Proprietary EULA |
| Website | [1] |
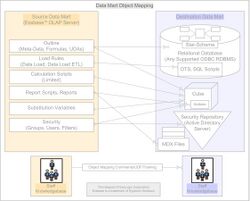
CubePort is a commercial software application that converts from Oracle Essbase to the analogous Microsoft product Microsoft Analysis Services, which is built into Microsoft SQL Server. This application achieves this through various analogy mapping techniques, and is a standard client-server application that runs on a Windows computer but may connect to non-Windows servers. CubePort converts the various OLAP structures and syntaxes in the source through an extraction process, interprets, and recreates in the target. The objective is to simulate exactly the behavior of the original source system to the target system.
The application also includes UI phases such as Authentication, Questions, Extraction, and Verification. Substantial testing normally occurs after the conversion process prior to posting the objects to production.
History
The software was released widely in 2005. CubePort represents the first product of its kind in the Business intelligence platform migration space. The product was design and created to provide an organization with the ability to move their Business Intelligence assets from one platform to another.
Unlike the RDBMS (relational databases) world where there exists the commonplace ability to migrate from one RDBMS product type to another, in the Business Intelligence or OLAP product space, this capability is currently not found in the marketplace.
Usage Motivations
Motivations for migrating from one Business Intelligence platform to another, regardless of whether this is achieved through automated or manual methods, vary from implementation to implementation, and may include one or more of the following motivations:
- Reduction of licensing or recurring maintenance expense
- Increase of detail-level of the cube
- Increase of the user count
- Elimination of cube load and calculation time constraints
- Elimination of pervasive vendor lock-in scenario
- Standardization towards Microsoft BI platform, where appropriate
Objects Converted
These standard objects in a cube are converted by the software with varying levels of robustness:
- Cube Outline
- Cube Data Loads and Dimension Builds
- Cube Security Model
- Cube Substitution Variables
- Cube Calculation Scripts
- Cube Report Scripts
The output objects of a successful run of CubePort are: A relational Star schema and/or relational Snowflake schema, OLAP cube, Etl load packages, MDX (Multidimensional Expressions) files, and others.
See also
External links
- SSAS Info Analysis Services Information Page
- Product Preview on CubePort
- Corporate Product Page
- Microsoft's Mosha Pasumansky's Analysis Services Product Page
- Microsoft Solution Page
- Mosha Pasumanky's BI Blog