Template:Comparison satellite navigation orbits
From HandWiki
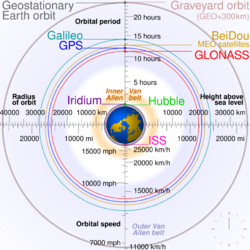
Comparison of geostationary, GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, Compass (MEO), International Space Station, Hubble Space Telescope, Iridium constellation and graveyard orbits, with the Radiation|Radiation
belt]]s and the Earth to scale.[lower-alpha 1] The Moon's orbit is around 9 times as large as geostationary orbit.[lower-alpha 2] (In the SVG file, hover over an orbit or its label to highlight it; click to load its article.)]]
References
- ↑ Orbital periods and speeds are calculated using the relations 4π2R3 = T2GM and V2R = GM, where R = radius of orbit in metres, T = orbital period in seconds, V = orbital speed in m/s, G = gravitational constant ≈ 6.673×10−11 Nm2/kg2, M = mass of Earth ≈ 5.98×1024 kg.
- ↑ Approximately 8.6 times (in radius and length) when the moon is nearest (363 104 km ÷ 42 164 km) to 9.6 times when the moon is farthest (405 696 km ÷ 42 164 km).
