Engineering:Northrop Beta
| Northrop Beta | |
|---|---|
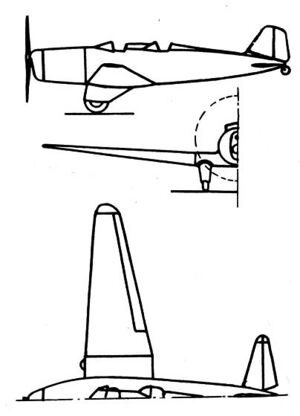
| |
| Northrop Beta 3-view drawing from L'Aerophile Salon 1932 | |
| Role | Sporting Monoplane |
| Manufacturer | Northrop |
| Designer | Don R. Berlin |
| First flight | 3 March 1931 |
| Number built | 2 (1 Beta 3 and 1 Beta 3D)[1] |
| Variants | Northrop Alpha Northrop Gamma |
The Northrop Beta was an American single-engine, all-metal, low-wing sporting monoplane built in 1931.[1]
Design and development
The Beta was a two-seater with a 160 hp (119 kW) Menasco Buccaneer inline engine. The first aircraft registered as NX963Y (later NC963Y) crashed in California. The second aircraft, N12214, was built as a single-seater and fitted with a 300 hp (224 kW) Pratt & Whitney Wasp Jr. radial engine, and became the first aircraft of such power to exceed 200 mph (322 km/h).[1] Only two were built.
The aircraft was flown to Wichita for sister company Stearman Aircraft to use as a demonstrator but with the poor economy at the time, none were sold. The aircraft was sold to a wealthy pilot in New York and during its delivery, it passed through Wright Field in order to allow a thorough examination by Army Air Corps Engineers as the Air Corps was still using obsolete biplanes.
After being rarely flown during 1932, the aircraft was sold to a new owner who kept it at Roosevelt Field until it was flipped over at a nearby airport. The aircraft was repaired at the Stearman factory in Wichita and used as an experimental test platform for various flap designs until it crashed due to a wing structural failure on May 4, 1934.
Specifications (Beta 3D)
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 66 m (21 ft 8 in)
- Wingspan: 9.75 m (32 ft 0 in)
- Powerplant: 1 × Pratt & Whitney Wasp Jr. radial, 224 kW (300 hp)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 341 km/h (212 mph, 184 kn)
- Cruise speed: 297 km/h (185 mph, 160 kn)
See also
Related development
References
 |

