Engineering:Backstrom EPB-1 Flying Plank
| EPB-1 Flying Plank | |
|---|---|

| |
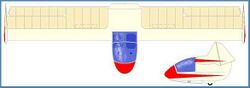
| WPB-1 Flying Plank II at the Airpower Museum | |
| Role | Glider |
| National origin | United States |
| Designer | Al Backstrom |
| Introduction | 1954 |
| Status | Plans still available |
| Number built | 16 |
The Backstrom EPB-1 Flying Plank is an American mid-wing, single seat, tailless glider that was designed by Al Backstrom, with assistance from Phil Easley and Jack Powell in 1954 and made available as plans for amateur construction.[1][2]
Design and development
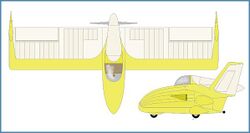
The Flying Plank was intended to be an aircraft that could be built at home, that would be of minimum size and yet still provide reasonable soaring performance. The prototype Plank featured tip rudders and was used for drag-reduction tests conducted at Mississippi State University before it was retired. The EPB-1 designation indicates the design team's last names.[1][2]
The EPB-1 is constructed with a wooden structure, with doped aircraft fabric covering. The landing gear is a monowheel, with a nose skid.[1][2]
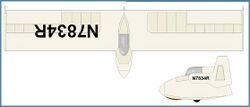
The "A" model was described in the plans sold and retained the twin tip rudders of the EPB-1, although some were built with a single fin and rudder assembly attached to the cockpit rear. At least one two-place side-by-side seating version was built in Australia , and another as a motor glider. The standard wingspan is 25 ft (7.6 m), but versions have been built with spans up to 30.5 ft (9.3 m).[1][2]
Operational history
In March 2011 two EPB-1s were still registered in the USA, including the one in the National Soaring Museum.[3]
Variants
- EPB-1
- Initial prototype with dual tip rudders[1][2]
- EPB-1A
- Standard model built from plans, also with dual tip rudders[1][2]
- EPB-1C
- Model modified by Al Cleave, featuring a centrally-mounted fin and rudder.[2][4]
- EPB-1H
- Model modified with a different airfoil, was not successful, dismantled.[2]
- WPB-1 Powered Plank
- Also known as the Flying Plank II, motor glider version[5][6]
Aircraft on display
- National Soaring Museum - EPB-1A and EPB-1C[7]
Specifications (EPB-1A)
Data from Sailplane Directory and Soaring[1][2]
General characteristics
- Crew: one
- Wingspan: 25 ft 0 in (7.62 m)
- Wing area: 100 sq ft (9.3 m2)
- Aspect ratio: 6.25
- Airfoil: Abrial 15%
- Empty weight: 150 lb (68 kg)
- Gross weight: 350 lb (159 kg)
Performance
- Maximum glide ratio: 20:1 at 60 mph (97 km/h)
- Rate of sink: 210 ft/min (1.1 m/s) at 47 mph (76 km/h)
- Wing loading: 3.5 lb/sq ft (17 kg/m2)
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Activate Media (2006). "Flying Plank EPB-1A Bachstrom (sic)". Archived from the original on 5 April 2012. https://web.archive.org/web/20120405061250/http://www.sailplanedirectory.com/PlaneDetails.cfm?PlaneID=104. Retrieved 21 March 2011.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 Said, Bob: 1983 Sailplane Directory, Soaring Magazine, page 12. Soaring Society of America, November 1983. USPS 499-920
- ↑ Federal Aviation Administration (March 2011). "Make / Model Inquiry Results". http://registry.faa.gov/aircraftinquiry/AcftRef_Results.aspx?Mfrtxt=&Modeltxt=EPB-1&PageNo=1. Retrieved 21 March 2011.
- ↑ [1][yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}], The EPB-1C, Sport Aviation, 1965, January, p. 31
- ↑ "Backstrom Flying Plank EPB-1 / Backstrom WPB-1 Powered Plank". http://all-aero.com/index.php/59-planes-b-c/1300-backstrom-flying-plank-epb-1a.
- ↑ Federal Aviation Administration (March 2011). "Make / Model Inquiry Results". https://registry.faa.gov/AircraftInquiry/Search/NNumberResult?nNumberTxt=20wb. Retrieved 1 June 2023.
- ↑ National Soaring Museum (2011). "Sailplanes in Our Collection". Archived from the original on 16 May 2011. https://web.archive.org/web/20110516142717/http://www.soaringmuseum.org/collection.html. Retrieved 26 February 2011.
External links
 |