Social:Naqsh-e Rostam
Naqsh-e Rostam (Persian: نقش رستم [ˌnæɣʃeɾosˈtæm]) is an ancient necropolis located about 12 km northwest of Persepolis, in Fars Province, Iran, with a group of ancient Iranian rock reliefs cut into the cliff, from both the Achaemenid and Sassanid periods. It lies a few hundred meters from Naqsh-e Rajab, with a further four Sassanid rock reliefs, three celebrating kings and one a high priest.
Naqsh-e Rostam is the necropolis of the Achaemenid dynasty (c. 550–330 BC), with four large tombs cut high into the cliff face. These have mainly architectural decoration, but the facades include large panels over the doorways, each very similar in content, with figures of the king being invested by a god, above a zone with rows of smaller figures bearing tribute, with soldiers and officials. The three classes of figures are sharply differentiated in size. The entrance to each tomb is at the center of each cross, which opens onto a small chamber, where the king lay in a sarcophagus.[1]
Well below the Achaemenid tombs, near ground level, are rock reliefs with large figures of Sassanian kings, some meeting gods, others in combat. The most famous shows the Sassanian king Shapur I on horseback, with the Roman Emperor Valerian bowing to him in submission, and Philip the Arab (an earlier emperor who paid Shapur tribute) holding Shapur's horse, while the dead Emperor Gordian III, killed in battle, lies beneath it (other identifications have been suggested). This commemorates the Battle of Edessa in 260 AD, when Valerian became the only Roman Emperor who was captured as a prisoner of war, a lasting humiliation for the Romans. The placing of these reliefs clearly suggests the Sassanid intention to link themselves with the glories of the earlier Achaemenid Empire.[2]
Monuments
The oldest relief at Naqsh-e Rostam dates back to c. 1000 BC. Though it is severely damaged, it depicts a faint image of a man with unusual head-gear, and is thought to be Elamite in origin.[3] The depiction is part of a larger mural, most of which was removed at the command of Bahram II. The man with the unusual cap gives the site its name, Naqsh-e Rostam ("Rustam Relief" or "Relief of Rustam"), because the relief was locally believed to be a depiction of the mythical hero Rustam.
Achaemenid tombs
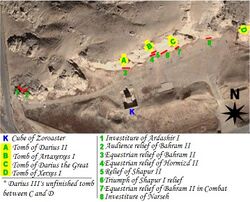
Four tombs belonging to Achaemenid kings are carved out of the rock face at a considerable height above the ground. The tombs are sometimes known as the Persian crosses, after the shape of the facades of the tombs. The entrance to each tomb is at the center of each cross, which opens onto a small chamber, where the king lay in a sarcophagus. The horizontal beam of each of the tomb's facades is believed to be a replica of a Persepolitan entrance.
One of the tombs is explicitly identified, by an accompanying inscription (“parsa parsahya puthra ariya ariyachitra”, meaning, “a Parsi, the son of a Parsi, an Aryan, of Aryan family),[4] as the tomb of Darius I (c. 522-486 BC). The other three tombs are believed to be those of Xerxes I (c. 486-465 BC), Artaxerxes I (c. 465-424 BC), and Darius II (c. 423-404 BC) respectively. The order of the tombs in Naqsh-e Rostam follows (left to right): Darius II, Artaxerxes I, Darius I, Xerxes I. The matching of the other kings to tombs is somewhat speculative; the relief figures are not intended as individualized portraits.[1]
A fifth unfinished one might be that of Artaxerxes III, who reigned at the longest two years, but is more likely that of Darius III (c. 336-330 BC), the last king of the Achaemenid Dynasts. The tombs were looted following the conquest of the Achaemenid Empire by Alexander the Great.
Darius I inscription
An inscription by Darius I, from c.490 BCE, generally referred to as the "DNa inscription" in scholarly works, appears in the top left corner of the facade of his tomb. It mentions the conquests of Darius I and his various achievements during his life. Its exact date is not known, but it can be assumed to be from the last decade of his reign.[5] Like several other inscriptions by Darius, the territories controlled by the Achaemenid Empire are clearly listed, in particular the areas of the Indus and Gandhara in India, referring to the Achaemenid occupation of the Indus Valley.[6]
| English translation | Original |
|---|---|
|
Ka'ba-ye Zartosht

Ka'ba-ye Zartosht (meaning the "Cube of Zoroaster") is a 5th-century B.C Achaemenid square tower. The structure is a copy of a sister building at Pasargadae, the "Prison of Solomon" (Zendān-e Solaymān). It was built either by Darius I (r. 521–486 BCE) when he moved to Persepolis, by Artaxerxes II (r. 404–358 BCE) or Artaxerxes III (r. 358–338 BCE). The building at Pasargadae is a few decades older. There are four inscriptions in three languages from the Sasanian period on the lower exterior walls. They are considered among the most important inscriptions from this period.
Several theories exist regarding the purpose of the Ka'ba-ye Zartosht structure.[12]
Sassanid reliefs
Seven over-life sized rock reliefs at Naqsh-e Rostam depict monarchs of the Sassanid period. Their approximate dates range from 225 to 310 AD, and they show subjects including investiture scenes and battles.
Investiture relief of Ardashir I, c. 226–242
The founder of the Sassanid Empire is seen being handed the ring of kingship by Ohrmazd. In the inscription, which also bears the oldest attested use of the term Iran, Ardashir admits to betraying his pledge to Artabanus V (the Persians having been a vassal state of the Arsacid Parthians), but legitimizes his action on the grounds that Ohrmazd had wanted him to do so.
The word ērān is first attested in the inscriptions that accompany the investiture relief of Ardashir I (r. 224–242) at Naqsh-e Rostam. In this bilingual inscription, the king calls himself "Ardashir, king of kings of the Iranians" (Middle Persian: ardašīr šāhān šāh ī ērān; Parthian: ardašīr šāhān šāh ī aryān).
Triumph of Shapur I, c. 241–272)
This is the most famous of the Sassanid rock reliefs, and depicts the victory of Shapur I over two Roman emperors, Valerian and Philip the Arab. Behind the king stands Kirtir, the mūbadān mūbad ('high priest'), the most powerful of the Zoroastrian Magi during the history of Iran.[13] A more elaborate version of this rock relief is at Bishapur.
"Grandee" relief of Bahram II, c. 276–293
On each side of the king, who is depicted with an oversized sword, figures face the king. On the left, stand five figures, perhaps members of the king's family (three having diadems, suggesting they were royalty). On the right, stand three courtiers, one of which may be Kartir. This relief is to the immediate right of the investiture inscription of Ardashir, and partially replaces the much older relief that gives the name of Naqsh-e Rostam.
Two equestrian reliefs of Bahram II, c. 276–293
The first equestrian relief, located immediately below the fourth tomb (perhaps that of Darius II), depicts the king battling a mounted Roman enemy. The second equestrian relief, located immediately below the tomb of Darius I, is divided into two registers, an upper and a lower one. In the upper register, the king appears to be forcing a Roman enemy, probably Roman emperor Carus from his horse. In the lower register, the king is again battling a mounted enemy wearing a headgear shaped as an animal’s head, thought to be the vanquished Indo-Sassanian ruler Hormizd I Kushanshah.[14] Both reliefs depict a dead enemy under the hooves of the king's horse.
Hormizd I Kushanshah on the lower panel.[14]
Investiture of Narseh, c. 293–303
In this relief, the king is depicted as receiving the ring of kingship from a female figure that is frequently assumed to be the divinity Aredvi Sura Anahita. However, the king is not depicted in a pose that would be expected in the presence of a divinity, and it is hence likely that the woman is a relative, perhaps Queen Shapurdukhtak of Sakastan.
Equestrian relief of Hormizd II, c 303–309
This relief is below tomb 3 (perhaps that of Artaxerxes I) and depicts Hormizd forcing an enemy (perhaps Papak of Armenia) from his horse. Immediately above the relief and below the tomb is a badly damaged relief of what appears to be Shapur II (c. 309–379) accompanied by courtiers.
Archaeology
In 1923, the German archaeologist Ernst Herzfeld made casts of the inscriptions on the tomb of Darius I. Since 1946, these casts have been held in the archives of the Freer Gallery of Art and the Arthur M. Sackler Gallery, Smithsonian Institution, in Washington, DC.
Naqsh-e Rostam was excavated for several seasons between 1936 and 1939 by a team from the Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago, led by Erich Schmidt.[15]
See also
- Essaqwand Rock Tombs
- Persepolis
- Qadamgah (ancient site)
- Pasargadae and Tomb of Cyrus the Great
- Behistun Inscription
- Bishapur
- Istakhr
- Taq-e Bostan (rock reliefs of various Sassanid kings)
- List of colossal sculpture in situ
- Valley of the Kings
- Naqsh-e Rajab
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Cotterell, 162; Canepa, 57–59, 65–68
- ↑ Herrmann and Curtis; Canepa, 62, 65–68
- ↑ [1] Morteza KHANIPOOR et al, The reliefs of Naqš-e Rostam and a reflection on a forgotten relief, Iran, Historia i Świat, iss. 6, pp. 55-68, 2017
- ↑ "I am Darius". http://www.parsiana.com/current-issue/articles.aspx?id=YtNsF2zng3o=&issue=73.
- ↑ (in fr) Orientalia Lovaniensia Periodica. Instituut voor Oriëntalistiek.. 1974. p. 23. https://books.google.com/books?id=keVtAAAAMAAJ.
- ↑ Briant, Pierre (2002) (in en). From Cyrus to Alexander: A History of the Persian Empire. Eisenbrauns. p. 173. ISBN 9781575061207. https://books.google.com/books?id=lxQ9W6F1oSYC&pg=PA173.
- ↑ Tolman, Herbert Cushing (1893). A guide to the Old Persian inscriptions. New York, Cincinnati [etc.] American book company. p. 146. https://archive.org/stream/guidetooldpersia00tolmrich#page/146.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "DNa - Livius" (in en). http://www.livius.org/sources/content/achaemenid-royal-inscriptions/dna/?.
- ↑ Alcock, Susan E.; Alcock, John H. D'Arms Collegiate Professor of Classical Archaeology and Classics and Arthur F. Thurnau Professor Susan E.; D'Altroy, Terence N.; Morrison, Kathleen D.; Sinopoli, Carla M. (2001) (in en). Empires: Perspectives from Archaeology and History. Cambridge University Press. p. 105. ISBN 9780521770200. https://books.google.com/books?id=MBuPx1rdGYIC&pg=PA105.
- ↑ The Achaemenid Empire in South Asia and Recent Excavations in Akra in Northwest Pakistan Peter Magee, Cameron Petrie, Robert Knox, Farid Khan, Ken Thomas p.713-714
- ↑ (in en) NAQŠ-E ROSTAM – Encyclopaedia Iranica. http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/naqs-e-rostam.
- ↑ http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/kaba-ye-zardost
- ↑ Rome in the East: The Transformation of an Empire. Warwick Ball. page 120. Psychology Press, 16 Jan 2001.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Encyclopedia Iranica HORMOZD KUŠĀNŠĀH article
- ↑ [2] E. F. Schmidt, Persepolis III: The Royal Tombs and Other Monuments, Oriental Institute Publications 70, University of Chicago Press, 1970, ISBN:0-226-62170-7
References
- Canepa, Matthew P., "Topographies of Power, Theorizing the Visual, Spatial and Ritual Contexts of Rock Reliefs in Ancient Iran", in Harmanşah (2014), google books
- Cotterell, Arthur (ed), The Penguin Encyclopedia of Classical Civilizations, 1993, Penguin, ISBN:0670826995
External links
- Ernst Herzfeld Papers, Series 5: Drawings and Maps, Records of Naqsh-i Rustam Collections Search Center, S.I.R.I.S., Smithsonian Institution, Washington, D.C.
- Hubertus von Gall "NAQŠ-E ROSTAM" in Encyclopædia Iranica [3]
- Lendering, Jona (2009). "Naqsh-i Rustam". Amsterdam: Livius. http://www.livius.org/na-nd/naqsh-i-rustam/naqsh-i-rustam.html.
- Unknown (2005). "Naghsh-e-Rostam". http://landofaryan.atspace.com/rostam.htm.
- Herrmann, G. & Curtis, V. S. (2003). "Sasanian Rock Reliefs". Encyclopedia Iranica. Costa Mesa: Mazda. http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/sasanian-rock-reliefs.
 |