Software:Faustino (platform)
 | |
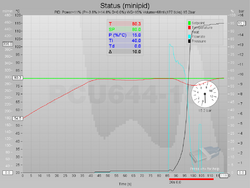 A screenshot of the faustino status monitor | |
| Developer(s) | http://emc.awardspace.com |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 1
/ September 14, 2009 |
| Written in | Java |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Type | Communication Software |
| License | Proprietary |
| Website | http://emc.awardspace.com |
Faustino is a physical computing platform geared towards process monitoring and control. The faustino platform consists of a single-board microcontroller with embedded analog and digital I/O support, an input module with LCD, sensors and actuators in form of solid state relays. The development software is based on Eclipse and WinAVR, a variant of GCC for AVR microcontrollers. For visual presentation of measurements, a XML-configured Windows status monitor application is available.
Hardware
The hardware is based on an Atmel AVR microcontroller which can be connected to a PC via a FTDI-USB-serial converter. An ATMega644 is used. The boards are powered by 6 V - 9 V AC and use an 18.4 MHz crystal oscillator.
Use of an AC power source permits zero cross detection on the secondary side of the power supply and therefore phase control (PFC) for connected solid state relays. The microcontroller is pre-programmed with a boot loader. It is programmed by its USB port and does not require an external programmer.
The faustino platform is geared towards measurement and control engineering by the hobby enthusiast. For that purpose, it is equipped with vibration resistant connectors, a wide temperature range (for example, silicone insulated leads are used), galvanic isolation of the PC interface and support for typical sensors such as ratiometric pressure sensors, thermocouples and a flow meter. Unlike other development platforms such as Arduino, only a few I/O pins of the microcontroller are unassigned and available for use with or by other circuits.
External links
 |

