Biology:Choreotrich
| Choreotrich | |
|---|---|
| |
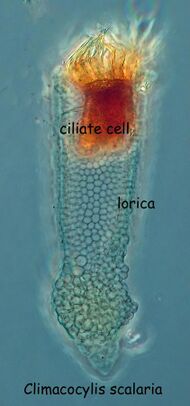
| A tintinnid[1] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Clade: | Diaphoretickes |
| Clade: | SAR |
| Clade: | Alveolata |
| Phylum: | Ciliophora |
| Class: | Spirotrichea |
| Subclass: | Choreotrichia Small & Lynn 1985 |
| Typical orders | |
| |
The choreotrichs are a group of small marine ciliates. Their name reflects the impression that they appear to dance ('choreo' as in choreography). The group includes the tintinnids,[2] which produce species-specific loricae (shells), and are important because these may be preserved as microfossils. The cyst forms have been suggested to be affiliated to Chitinozoans,[3] although other studies suggest Chitinozoans to have affinities to larger marine animals, and not tintinnids.[4] Often they have been included among the oligotrichs. Tintinnids seem to be an excessively specious group as over 400 living species have been described, based on characteristics of the lorica or shell.
Choreotrichs (including tintinnids) are part of the microzooplankton. Generally small (20–200 micrometres in size) organisms found in the plankton. They feed on small algae and serve as prey for larger organisms in the plankton such as copepods and larval fish.
References
- ↑ WoRMS: Climacocylis scalaria Brandt, 1906, World of Marine Species
- ↑ Capriulo, Gerard M. (1990) (in en). Ecology of Marine Protozoa. Oxford University Press. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-19-504316-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=61kWAQAAIAAJ&q=%22Choreotrich+(e.g.,+tintinnids)%22+.
- ↑ Reid, P.C.; John, A.W.G. (1981). "A possible relationship between chitinozoa and tintinnids". Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 34 (2): 251–262. doi:10.1016/0034-6667(81)90043-9.
- ↑ Gabbott, S.E.; Aldridge, R.J.; Theron, J.N. (1998). "Chitinozoan chains and cocoons from the Upper Ordovician Soom Shale lagerstatte, South Africa; implications for affinity". Journal of the Geological Society 155 (3): 447–452. doi:10.1144/gsjgs.155.3.0447.
Wikidata ☰ Q5105018 entry
 |

