Biology:Sesuvium maritimum
| Sesuvium maritimum | |
|---|---|

| |
| |
| Scientific classification Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Aizoaceae |
| Genus: | Sesuvium |
| Species: | S. maritimum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Sesuvium maritimum (Walter) Britton, Sterns & Poggenb.
| |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
Sesuvium maritimum is an annual herbaceous plant native to southeastern North America in the family Aizoaceae.[3] This species is commonly known as the annual or slender sea purslane or Puerto Rico Sea-purslane.[3][4][1] It can be found on sandy beaches, salt marshes, or other coastal regions.[4][5]
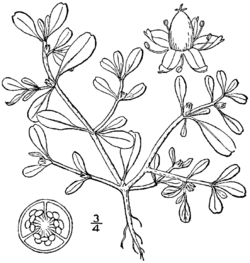
Description
Sesuvium maritimum is a succulent herb that can grow up to 30 cm tall, with smooth, glabrous leaves and white or pink inflorescences.[4] Its leaves are covered with dozens of fleshy projections known as papillae.[6] They are commonly found along the southeastern coast of North America from as far north as Rhode Island to southern regions of Mexico, Puerto Rico, Cuba, the Bahamas, and other surrounding islands.[3][5] It has an opposite or sub-opposite leaf arrangement composed of simple, oblanceolate or linear fleshy leaves that are about 1-2.5 cm long and 1–5 mm wide.[5] Furthermore, the leaves are known to be glabrous or rarely minutely papillose, the apex are rounded, acute, or obtuse with margins of the leaves being entire.[4] Flowers are actinomorphic and normally composed of 4–5 fused petals that form a cup-like structure.[7] Within the flower are 5 stamens, usually with a pink coloration, and a partially inferior ovary.[8] Sepals are 2-3 mm long and attached near the top of the calyx tube.[4]
Fruits
They form a pyxis (dry dehiscent capsules) around 4–5 mm in length that appear soon after flowering and persist until September. Upon maturity the capsules will spit open.[7][9] The seeds produced are typically smooth and vary in color from black to brown, as well as, the amount produced can be between 30–50.[9]
Distribution
This plant is commonly present within costal regions of eastern US (Alabama, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Virginia, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Texas).[4] They reach far down as, southern regions of Mexico, Puerto Rico, Cuba, the Bahamas, and other surrounding islands.[3] Furthermore, it was found to be present in Kansas and Oklahoma.[9]
Taxonomy
The Sesuvium genus was named after the Gallic tribe Sesuvii, who resided in the Atlantic maritime region of France from around 58–50 BC.[10]
Conservation status
The slender sea purslane is currently endangered in New York state, Maryland, North Carolina, Kansas, and Southern Florida.[1][11] It is also considered vulnerable in the state of Virginia.[11] Globally, Sesuvium maritimum has a conservation status of G5 (globally secure).[12]
Uses
In the past, sea purslane were once used as medicine to treat scurvy and venomous wounds.[13] In addition, it's one of several plants that aid in the prevention of coastal erosion.[14]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Sesuvium maritimum". https://explorer.natureserve.org/Taxon/ELEMENT_GLOBAL.2.145489/Sesuvium_maritimum.
- ↑ "Sesuvium maritimum" (in en). Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/taxon/364610-1. Retrieved 15 April 2022.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Bohley, Katharina; Winter, Pieter J. D.; Kadereit, Gudrun (2017-03-01). "A Revision of Sesuvium (Aizoaceae, Sesuvioideae)". Systematic Botany 42 (1): 124–147. doi:10.1600/036364417x694575. ISSN 0363-6445. http://dx.doi.org/10.1600/036364417x694575.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 Boetsch, John R. (2002). "The Aizoaceae and Molluginaceae of the Southeastern United States". Castanea 67 (1): 42–53. ISSN 0008-7475. https://www.jstor.org/stable/4034315.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Radford, Albert E. (1968). Manual of the vascular flora of the Carolinas. Harry E. Ahles, C. Ritchie Bell. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press. ISBN 0-8078-1087-8. OCLC 355003. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/355003.
- ↑ "Mid-Atlantic Herbaria – Sesuvium maritimum". https://midatlanticherbaria.org/portal/taxa/index.php?taxon=101070&clid=3415.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Sesuvium maritimum (annual sea-purslane): Go Botany". https://gobotany.nativeplanttrust.org/species/sesuvium/maritimum/.
- ↑ "NameThatPlant.net: Sesuvium maritimum". http://www.namethatplant.net/plantdetail.shtml?plant=4091.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 "Sesuvium maritimum in Flora of North America @ efloras.org". http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=1&taxon_id=242415129.
- ↑ "Sea Purslane Guide – New York Natural Heritage Program". https://guides.nynhp.org/sea-purslane/.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "The Institute for Regional Conservation". https://regionalconservation.org/ircs/database/plants/PlantPage.asp?TXCODE=Sesumari.
- ↑ "Vascular Plants of North Carolina". https://auth1.dpr.ncparks.gov/flora/species_account.php?id=26.
- ↑ "Sanibel Salad: Sea Purslane" (in en-US). https://www.sanibelseaschool.org/experience-blog/2018/7/24/sanibel-salad-sea-purslane.
- ↑ "Sea purslane research at Mote Aquaculture Research Park – Responsible Seafood Advocate" (in en-US). https://www.globalseafood.org/advocate/sea-purslane-research-at-mote-aquaculture-research-park/.
Wikidata ☰ Q4413064 entry
 |


