Biology:Actinotus helianthi
| Actinotus helianthi | |
|---|---|

| |
| At Henry Head Track, Botany Bay National Park | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Apiales |
| Family: | Apiaceae |
| Genus: | Actinotus |
| Species: | A. helianthi
|
| Binomial name | |
| Actinotus helianthi Labill.
| |
| |
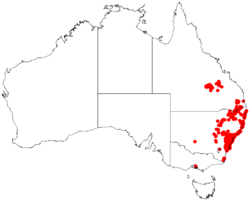
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
Actinotus helianthi, known as the flannel flower, is a common species of flowering plant native to the bushland around Sydney. It was named and first described by the French botanist Jacques Labillardière in his Novae Hollandiae Plantarum Specimen the first general flora of Australia. According to historian Edward Duyker Labillardière could not have collected the type specimen personally and might have received it from Jean-Baptiste Leschenault de La Tour botanist on the expedition of Nicolas Baudin or another early French visitor to New South Wales.[1]
Despite its appearance, it is not a member of the daisy family but rather a species of the Apiaceae (formerly Mackinlayaceae) family, the same family as the carrot. Its generic name, meaning "furnished with rays", is derived from the Greek stem aktin-/ακτιν- "ray" or "spoke of a wheel" or "sunbeam",[2][3] while its specific epithet is derived from its resemblance to the genus Helianthus.[4] An iconic Sydney plant, its floral display has horticultural appeal which has seen limited use in the home garden and cut flower industry. It grows alongside the related lesser flannel flower (A. minor).
Description
The flannel flower is generally a herbaceous shrub growing up to 50 cm (18 in) high, although rare specimens can be found to be 1.5 m (5 feet) high.[3] The stem, branches and leaves of the plant are a pale grey in colour, covered in downy hair (rather like flannel in texture). The attractively lobed leaves are up to 10 cm (4 in) long and 7 cm (3 in) wide, with daisy-shaped flowerheads around 5 or occasionally 8 cm (2–3 in) in diameter. The bracts are cream to white in colour. Flowering occurs in spring and may be profuse after bushfires.[4]
Flannel flowers grow in sandstone heathland in coastal New South Wales and Queensland, and are commonly seen around the Sydney basin in spring.
Cultivation
Plants may be propagated by seed or cutting and grow in a well-drained sunny position, and are suitable for use in a rockery or cottage garden. The Mount Annan Botanic Garden has been involved in selecting and breeding cultivars for the home garden and the cut flower industry.[5] One selection was named Actinotus 'Federation Star', and was chosen to be the New South Wales floral emblem for the Centenary of Federation (1901–2001).
Popular culture
The flannel flower is an iconic Sydney plant and has been used in imagery and art since colonial times.
In St Bede's Church in the Sydney suburb of Drummoyne, the early 20th century work The Waratah Window by Alfred Handel depicts Australian native flowers, including the waratah, emblem of the state of New South Wales, and flannel flowers, Christmas bells and wattles. Flannel flowers are the emblem of the Sydney Bush Walkers' club established in 1927.
References
- ↑ Duyker (2003) p. 232.
- ↑ Liddell & Scott (1980). Greek-English Lexicon, Abridged Edition. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK. ISBN 0-19-910207-4. https://archive.org/details/lexicon00lidd.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Blombery, Alec (1965). "The genus Actinotus". Australian Plants (ASGAP) 3 (22): 63–65. ISSN 0005-0008.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Elliot, Rodger W.; Jones, David L. (1982). "A-Ca". in Elliot, Rodger W.. Encyclopaedia of Australian Plants suitable for cultivation. 2. Lothian Publishing. pp. 1–507. ISBN 0-85091-143-5.
- ↑ von Richter, L. and C. Offord. (1998). Flannel Flowers. In: The New Rural Industries. (Ed. K.W. Hyde). p 505–511. (RIRDC: Canberra).
External links
- ASGAP page on Actinotus helianthi
- ANBG page on Actinotus helianthi, with note on 'Federation Star'
- Labillardière, Jacques Julien Houtou de (1804) (in la). Novae Hollandiae Plantarum Specimen. Paris: Dominæ Huzard. https://archive.org/details/mobot31753002794516., see Novae Hollandiae Plantarum Specimen
Wikidata ☰ Q4677017 entry
 |




