Biology:Acacia rigens
| Acacia rigens | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Subfamily: | Caesalpinioideae |
| Clade: | Mimosoid clade |
| Genus: | Acacia |
| Species: | A. rigens
|
| Binomial name | |
| Acacia rigens A.Cunn. ex G.Don[1]
| |
| |
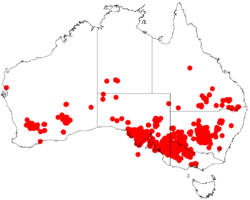
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Acacia rigens, commonly known as nealie, is an erect or spreading shrub or small tree that is endemic to Australia .[2][3] Other common names include needle wattle, needlebush acacia, nealia and nilyah.[3]
Description
Plants typically grows to a height of 1 to 6 m (3 ft 3 in to 19 ft 8 in) and have rigid, terete phyllodes that are between 3 and 13 cm (1.2 and 5.1 in) in length. The bright yellow flowerheads appear in groups of up to four in the axils of the phyllodes. The simple inflorescences have resinous and spherical flower-heads with a diameter of 4 to 7 mm (0.16 to 0.28 in) and contain 20 to 30 bright yellow coloured, 5-merous flowers that appear between July and December in the species' native range, followed by curled, twisted or coiled seed pods which are 4 to 10 cm (1.6 to 3.9 in) long and 2 to 3 mm (0.079 to 0.118 in) wide.[2][3]
Taxonomy
The species was first formally described in 1832 by botanist Allan Cunningham.[1] It resembles Acacia havilandiorum but has longer phyllodes and 4-merous flowers. The specific epithet is thought to be a reference to the rigidity of the phyllodes.[3]
Distribution
The species occurs on red earth, sandy or shaly soils in mallee and woodland in southern Western Australia, South Australia, Victoria, New South Wales and Queensland.[3][4]
Cultivation
The species is fast-growing and is both frost and drought tolerant, rarely requiring watering after establishment. It is adaptable to most soils and is best suited to a position in full sun or light shade.[5]
The larvae of the double-spotted lineblue butterfly feed on this species.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Acacia rigens". Australian Plant Name Index (APNI), IBIS database. Centre for Plant Biodiversity Research, Australian Government, Canberra. http://www.anbg.gov.au/cgi-bin/apni?TAXON_NAME=Acacia+rigens. Retrieved 2010-09-07.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Acacia rigens". FloraBase. Western Australian Government Department of Parks and Wildlife. https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/browse/profile/3522.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 "Acacia rigens". PlantNET - New South Wales Flora Online. Royal Botanic Gardens & Domain Trust, Sydney Australia. http://plantnet.rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au/cgi-bin/NSWfl.pl?page=nswfl&lvl=sp&name=Acacia~rigens. Retrieved 2010-09-07.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Acacia rigens". Electronic Flora of South Australia Fact Sheet. State Herbarium of South Australia. http://www.flora.sa.gov.au/cgi-bin/texhtml.cgi?form=speciesfacts&keyname=Acacia+rigens. Retrieved 2010-09-07.
- ↑ Greig, D. (1987). The Australian Gardener's Wildflower Catalogue. Australia: Angus & Robertson. ISBN 978-0-207-15460-7.
Wikidata ☰ Q4671001 entry
 |

