Biology:Haplogroup C-B477
From HandWiki
Short description: Human Y-chromosome haplogroup
| Haplogroup C-B477 | |
|---|---|
| Possible place of origin | Sahul Shelf |
| Ancestor | (Grandparent)C1 |
| Descendants | C1b2a-M38 C1b2b-M347 |
| Defining mutations | B477 |
| Highest frequencies | Papuan people, Indigenous Australians, Melanesian people, Polynesian people |
Haplogroup C-B477, also known as Haplogroup C1b2, is a Y-chromosome haplogroup. It is one of two primary branches of Haplogroup C1b, one of the descendants of Haplogroup C1.
It is distributed in high frequency in Indigenous Australians, Papuan people, Melanesian people, and Polynesian people.
Subgroups
Frequency
C-M38
C-M347
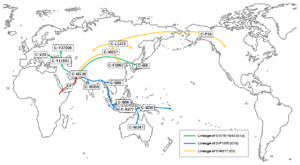
Migration history
Haplogroup C-B477 took South route after the Out of Africa through Indian subcontinent to Sahul Shelf.[8] C-M38 was born 49,600 years before present around New Guinea.[9]
References
- ↑ Hudjashov, GExpression error: Unrecognized word "etal". (May 2007). ""(May 2007). "Revealing the prehistoric settlement of Australia by Y chromosome and mtDNA analysis". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104 (21): 8726–30. doi:10.1073/pnas.0702928104. PMID 17496137.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 Kayser, MExpression error: Unrecognized word "etal". (February 2003). ""(February 2003). "Reduced Y-chromosome, but not mitochondrial DNA, diversity in human populations from West New Guinea". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 72 (2): 281–302. doi:10.1086/346065. PMID 12532283.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 Kayser, MExpression error: Unrecognized word "etal". (July 2008). ""(July 2008). "The impact of the Austronesian expansion: evidence from mtDNA and Y chromosome diversity in the Admiralty Islands of Melanesia". Mol. Biol. Evol. 25 (7): 1362–74. doi:10.1093/molbev/msn078. PMID 18390477.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 Cox, MPExpression error: Unrecognized word "etal". (October 2007). "A Polynesian motif on the Y chromosome: population structure in remote Oceania". Hum. Biol. 79 (5): 525–35. doi:10.1353/hub.2008.0004. PMID 18478968.
- ↑ "Maori origins, Y-chromosome haplotypes and implications for human history in the Pacific". Hum. Mutat. 17 (4): 271–80. April 2001. doi:10.1002/humu.23. PMID 11295824.
- ↑ Hudjashov, G.; Kivisild, T.; Underhill, P. A.; Endicott, P.; Sanchez, J. J.; Lin, A. A.; Shen, P.; Oefner, P. et al. (2007). "Revealing the prehistoric settlement of Australia by Y chromosome and mtDNA analysis". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 104 (21): 8726–30. doi:10.1073/pnas.0702928104. PMID 17496137. Bibcode: 2007PNAS..104.8726H.
- ↑ Kayser, M; Brauer, Silke; Weiss, Gunter; Schiefenhövel, Wulf; Underhill, Peter; Shen, Peidong; Oefner, Peter; Tommaseo-Ponzetta, Mila et al. (2003). "Reduced Y-Chromosome, but Not Mitochondrial DNA, Diversity in Human Populations from West New Guinea". The American Journal of Human Genetics 72 (2): 281–302. doi:10.1086/346065. PMID 12532283.
- ↑ 崎谷満『DNA・考古・言語の学際研究が示す新・日本列島史』(勉誠出版 2009年)(in Japanese)
- ↑ Scheinfeldt, L.; Friedlaender, F; Friedlaender, J; Latham, K; Koki, G; Karafet, T; Hammer, M; Lorenz, J (2006). "Unexpected NRY Chromosome Variation in Northern Island Melanesia". Molecular Biology and Evolution 23 (8): 1628–41. doi:10.1093/molbev/msl028. PMID 16754639.
 |