Place:Islamic Emirate of Byara
Islamic Emirate of Byara میرنشینی ئیسلامی بیارە | |
|---|---|
| 2001-2003 | |
|
Flag | |
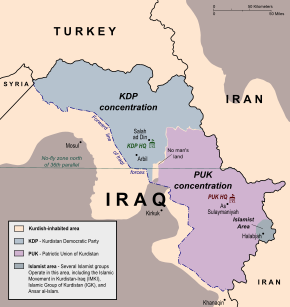 Islamic Emirate of Byara (black) at their peak, controlling the entire Halabja Governorate | |
| Status | Unrecognized independent state (2001–2003) |
| Capital and largest city | Byara |
| Official languages | Kurdish |
| Religion | Sunni Islam |
| Government | Islamic Emirate |
| Emir | |
• 2001–2003 | Mullah Krekar |
| Deputies | |
• 2001-2003 | Wirya Salih |
• 2001-2003 | Ali Bapir |
| History | |
• Established | September 2001 |
• Disestablished | March 30, 2003 |
| Currency | Iranian rial, Iraqi dinar (de facto) |
| Today part of | Iraqi Kurdistan |
The Islamic Emirate of Byara was a short-lived unrecognized Kurdish Islamic state ruled by Sharia law which declared independence from Iraq in 2001 and ended in 2003.
Foundation
In September 2001, in the Byara District, located in the Avroman region, a Kurdish jihadist group called Ansar al-Islam set up the Islamic Emirate of Byara, with the city of Byara as its capital. Mullah Krekar, leader of Ansar al-Islam, was the Emir of the Emirate, while Wirya Salih and Ali Bapir were his deputies. The emirate was the first time that Kurdish-Islamic nationalists succeeded at their goal, establishing a Kurdish state under Sharia. With the area under a de facto embargo from all sides, Kurdish jihadists from Iran gave vital cross-border support to the Emirate, setting up networks that illegally smuggled to the area and aided the Emirate.[1][2][3][4][5]
Life under the Islamic Emirate
Ansar al-Islam fighters in the Islamic Emirate of Byara embraced both their Kurdish and Muslim identities and advocated for a religious, cultural, and traditional lifestyle, hence why Ansar al-Islam fighters wore Kurdish clothes and spoke only in Kurdish, and encouraged their supporters to do the same. It was also reported that Ansar al-Islam committed inhumane atrocities against civilians, including extreme persecution of non-Muslims, enforcing strict Sharia law, destroying anything they claimed to be "un-Islamic", and desecrating Sufi shrines. Human Rights Watch accused Ansar al-Islam of torturing prisoners and executing any captured Peshmerga, Iraqi Army, US Army, or any foreign soldiers, usually by beheading.[6][7][8] The IRGC were accused of ignoring Ansar al-Islam's terrorist activities, as well as allowing Ansar al-Islam fighters to cross the borders and hide in Iran.[3]
Collapse
The Emirate ended after the United States launched Operation Viking Hammer in 2003. After the loss of the Emirate, Ansar fighters gathered at the Iran–Iraq border, where the IRGC ignored the Kurdish jihadists' activity, and Iranian Kurds who gave Ansar fighters asylum in Iran got approval from Iranian authorities, only if the jihadists arrived secretly and quietly, and would be housed in remote areas. The IRGC warned Iranian Kurds who were housing jihadists that if they were seen publicly, they would be arrested and sent back to Iraq. The IRGC also wanted the treatment of wounded fighters to be done secretly. Some Kurdish jihadists brought their families with them to Iran; some were detained by authorities for two brief weeks, and then were released and allowed to stay. It was also alleged that Ansar al-Islam made a deal with Iranian authorities that they would not commit any terrorism or attack any Iranians in order to be allowed to stay. Some jihadists settled in Iran, with others returning to Iraq, either joining other jihadist groups, or quitting the jihadist lifestyle.[1][2][3][9][10][11]
In late 2016, around the 15th anniversary of Byara, Mullah Krekar said that "I hope we separate from Iraq as soon as possible. I would support it wholeheartedly. We were annexed to the Iraqi state under force in 1921, a state that is a failed state in every sense. The first time Iraq purchased aircraft, they bombed the Kingdom of Kurdistan and Sulaymaniyah. If a tiny part of Kurdistan is separated from Iraq and declares independence, I will endorse it fully. When Mauritania declared independence, they didn't even have a building to wave their flag upon, but still they declared independence." He also said that he holds no negativity against any Kurdish government officials, and that many of his friends and family are in the Kurdish government. Hoshyar Zebari confirmed that the Kurdish government made peace with Krekar.[12]
See also
- Kurdish emirates
- Islamic Emirate of Kunar
- Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan (1996–2001)
- Islamic Emirate of Rafah
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Komal should ‘shed’ Islamic label: party leader". https://www.rudaw.net/english/kurdistan/03092020.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "How ISIS Infiltrated Iranian Kurdistan". https://iranwire.com/en/features/64660.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Journey to jihad: Iran’s Sunni Kurds fighting a holy war in Idlib". https://www.rudaw.net/english/middleeast/syria/23062020.
- ↑ "Iraqi political groupings and individuals". http://middleeastreference.org.uk/iraqiopposition.html#igk.
- ↑ Ram, Sunil (April 2003). "The Enemy of My Enemy: The odd link between Ansar al-Islam, Iraq and Iran". The Canadian Institute of Strategic Studies. http://www.ciss.ca/Comment_EnemyofMyEnemy.pdf.
- ↑ "Ansar al-Islam in Iraqi Kurdistan (Human Rights Watch Backgrounder, )". https://www.hrw.org/legacy/backgrounder/mena/ansarbk020503.htm#Armed+Islamist+groups+in+Iraqi+Kurdistan.
- ↑ "Ansar al-Islam in Iraqi Kurdistan". Human Rights Watch. https://www.hrw.org/backgrounder/mena/ansarbk020503.htm.
- ↑ Brynjar, Lia. Understanding Jihadi Proto-States - JSTOR. https://www.jstor.org/stable/26297412.
- ↑ Masters of Chaos, Chapter 13 p. 7
- ↑ John Pike. "Ansar al Islam (Supporters of Islam)". http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/world/para/ansar_al_islam.htm.
- ↑ "Radical Islam in Iraqi Kurdistan: The Mouse that Roared?". International Crisis Group. 2014-02-07. http://www.crisisgroup.org/en/regions/middle-east-north-africa/iraq-iran-gulf/iraq/B004-radical-islam-in-iraqi-kurdistan-the-mouse-that-roared.aspx.
- ↑ Mahmud Yasin Kurdi (29 September 2016). "Time has come to break from Iraq, says radical Kurdish cleric Mulla Krekar". http://rudaw.net/english/interview/29092016.



