Engineering:Soft plastic bait
Soft plastic bait, commonly known as soft lure, soft plastics, plastic bait, worm lure or just worm, is any of a range of elastomer-based fishing lures termed so because of their flexible, flesh-like texture. Soft lures are available in a large range of colours, sizes and particularly shapes, and are typically impaled directly onto a fishing hook like an ordinary bait.
Designed to imitate bait fishes or other aquatic invertebrates (mostly worms) that are ubiquitous natural foods for carnivorous/omnivorous fishes, the realistic texture and versatility combined with simple and economical production, as well as the freedom from handling live baits and having to keep baits fresh in wet containers, has led soft lures to become a standard article of modern fishing tackle, frequently used in conjunction with a jighead or as part of a sophisticated rig design (e.g. the Texas and Carolina rigs). It is also not uncommon to see soft lures impregnated with chemical attractants (e.g. dimethyl-β-propiothetin) to better entice fish olfactorily.
History
Soft plastics found their origins in the late 1950s and early 1960s, with small worms and grubs being molded from hard rubber. The stiff rubber used, as well as the basic shapes produced, did not allow the flexible action and effectiveness of modern soft plastics to be observed. The first soft plastic worm to have the soft and flexible qualities of modern lures was invented by Nick and Cosma Creme. After many experiments with different plastics, they perfected the worm in 1949. They called it the Creme Wiggle Worm (later renamed the Creme Scoundrel Worm). The worm came already rigged with 3 hooks, beads, and a propeller, the same way live worms were rigged. In 1967, Tom Mann introduced the Jelly Worm. They came in colors name after fruit, like Grape and Strawberry, with matching "fruity" scent added. They are still being made, today. In 1972, lure manufacturer Mister Twister patented the Curly Tail concept, utilizing the flexibility of silicone-based plastic to create a rubber lure with a more lifelike action and vastly improved fish-catching effectiveness. By the early to mid-1980s, high sales volumes of Mister Twister lures prompted many new entrants into the market, with competition soon leading to a broad and diverse selection of soft plastic lures being made available in a range of shapes, colors and sizes. Additionally, Tom Moore created the Touchdown Lure in 1974 in the back room of his store in Indiana. The Touchdown 6" Original was born with two hooks with naturally weedless weed guards and include a 12-inch leader with swivels and a sinker. Later a Pro version was created with two larger hooks and a 36-inch leader.
Uses
The diversity of soft plastic baits has enabled them to be used in many configurations, rigs and with various techniques. The original, and still most commonly seen use of soft plastics is as a simple lure, using a weighted hook known as a jighead. The hook of the jighead is threaded through the lure so that only the gape of the hook, and the eye, are exposed. Methods vary according to the shape of the plastic used, however is it most often cast and retrieved with short, sharp jerky motions applied by the angler through flicking the fishing rod tip. Experienced soft plastic anglers attempt to emulate the natural movement of the animal the soft plastic imitates, such as a prawn, baitfish or crawdad.
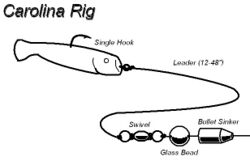
Soft plastics are also trolled and jigged in the same method as metal or hardbodied lures, and used as artificial baits in classic real-bait rigs. The many rigs, techniques and uses of soft plastic lures are as varied as the designs, colours and sizes they are available in. Specialised techniques and rigging methods have evolved from anglers targeting specific fish species or in particular areas, such as the Texas rig and Carolina rig. Tandem Rigs are designed to avoid losing fish that "short strike" the bait. A variation of the traditional Jig Head, called a Deep Darter Head, provide a sub surface "walk the dog" action on the soft plastic lure. The swimming tin, designed in the late 19th century to rig dead eels, is produced today to impart great action on large style soft baits like Hogy Lures 10-18 inch soft baits.
Modern variants
Today, soft plastic lures take on many forms and hybrids. Hardbody hybrid lures, with a solid plastic front half and soft plastic tail for lifelike action and appearance, are now common. These hybrids often use treble hooks, diving bibs and other features once restricted to hardbody lures. Concern over the instance of non-biodegradable plastics being lost in fragile water systems has prompted the creation of organic, biodegradable lures that retain the flexible, rubbery texture and action of traditional polymer soft plastic lures by tackle manufacturer Berkley. These new baits are based on different polymers, namely polyvinyl alcohol (PVOH), instead of the more usual polyvinyl chloride (PVC). There is much controversy in the angling community regarding the true nature of this new form of organic soft plastic, which has led to the use of such lures being prohibited in some lure-only angling competitions. However, since PVOH is still a synthetic polymer, which at the grades used in the Berkley lures only dissolve in water temperatures above 60°C, however this does not mean that it is biodegradable. Research by the University of Illinois has highlighted that some baits can swell inside the fish once ingested by up to 200%, hindering digestion [1] Companies like Hogy Lures have also developed soy based, large style, soft plastic lures designed to target trophy class fish.
See also
References
 |