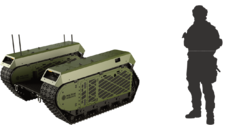
Engineering:THeMIS
| THeMIS | |
|---|---|
 Logistics variant of the THeMIS | |
| Type | Unmanned ground vehicle |
| Place of origin | Estonia |
| Service history | |
| In service | 2019–present |
| Used by | Estonian Defence Forces Royal Netherlands Army |
| Wars | Operation Barkhane Russian invasion of Ukraine |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Milrem Robotics |
| Manufacturer | Milrem Robotics |
| Produced | 2015–present |
| Variants | Logistics, Combat, ISR, EOD |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 1,630 kg (3,590 lb) |
| Length | 240 cm (94 in) |
| Width | 200 cm (79 in) |
| Height | 115 cm (45 in) |
Main armament | LMG, HMG, 40mm AGL, 30mm autocannon, ATGM, loitering munition launcher (Combat variant) |
| Engine | Electric engine, diesel generator |
| Payload capacity | 1,200 kg (2,600 lb) |
| Drive | Tracked |
| Ground clearance | 60 cm (24 in) |
Operational range | 1.5 km (0.93 mi) |
| Speed | 20 km/h (12 mph) |
THeMIS (Tracked Hybrid Modular Infantry System), unmanned ground vehicle (UGV), is a ground-based armed drone vehicle designed largely for military applications, and is built by Milrem Robotics in Estonia. The vehicle is intended to provide support for dismounted troops by serving as a transport platform, remote weapon station, IED detection and disposal unit etc.
Capability
The vehicle’s open architecture gives it multi-missions capability. The main purpose of the THeMIS Transport is to support onbase logistics and provide last mile resupply for fighting units on the front line. It supports infantry units by reducing their physical and cognitive load, increasing stand-off distance, force protection and survivability. THeMIS Combat UGVs provide direct fire support for manoeuvre forces acting as a force multiplier. With an integrated self-stabilizing remote-controlled weapon system, they provide high precision over wide areas, day and night, increasing stand-off distance, force protection and survivability. Combat UGVs can be equipped with light or heavy machine guns, 40 mm grenade launchers, 30mm autocannons and Anti-Tank Missile Systems. THeMIS ISR UGVs have advanced multi-sensor intelligence gathering capabilities. Their main purpose is to increase situational awareness, provide improved intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance over wide areas and battle damage assessment capability. The system can effectively enhance the work of dismounted infantry units, border guard and law enforcement agencies to collect and process raw information and decrease the reaction time for commanders. [1][2] THeMIS is capable of firing conventional machine gun ammunition or missile rounds[3][4][5]
History
On 29 September 2020, Estonia and the Netherlands officially announced that they are jointly acquiring 7 THeMIS UGVs. Both nations' armies have previously tested the system extensively.[6]
On 6 September 2022, Milrem Robotics delivered the THeMIS UGVs suited for casualty evacuation (CASEVAC) and transportation of supplies to Ukraine.[7] On November 22, 2022, German Ministry of Defense through Krauss-Maffei Wegmann (KMW) has signed a contract to deliver another 14 THeMIS unmanned ground vehicles (UGV) to Ukraine.[8]
The system has been exported to several NATO members and allies, including Australia, France, Germany, the Netherlands, Norway, the UK, Ukraine, and the US.[9][10]
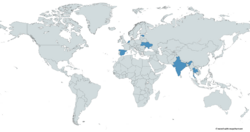
Operators
 Estonia
Estonia
- Estonian Defence Forces
 India
India
- Indian Armed Forces
 Netherlands
Netherlands
- Royal Netherlands Army[6]
 Spain
Spain
- Spanish Armed Forces, first unit received in August 2022.[11]
 Thailand
Thailand
- Royal Thai Army[12]
 Ukraine
Ukraine
- Armed Forces of Ukraine
See also
- Type-X, Milrem's 12-tonne robotic combat vehicle
References
- ↑ "This Estonian Tankette Is A Modular Body For War Robots" (in en). 4 March 2016. https://www.popsci.com/estonian-tankette-is-modular-body-for-war-robots.
- ↑ "Live Fire Test – Estonian Combat Robot - Defence24.com". https://www.defence24.com/live-fire-test-estonian-combat-robot.
- ↑ "IDEX 2019: Milrem Robotics unveils missile-armed THeMIS UGV | Jane's 360". https://www.janes.com/article/86733/idex-2019-milrem-robotics-unveils-missile-armed-themis-ugv.
- ↑ admin. "Weaponized Multi-Utility Unmanned Ground Vehicles" (in en-US). http://www.sadefensejournal.com/wp/?p=4614.
- ↑ "THeMIS Hybrid Unmanned Ground Vehicle" (in en-GB). https://www.army-technology.com/projects/themis-hybrid-unmanned-ground-vehicle/.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Eesti ja Holland ostavad Milrem Roboticsilt mehitamata maismaasõidukid" (in Estonian). Delfi. https://www.delfi.ee/news/paevauudised/eesti/eesti-ja-holland-ostavad-milrem-roboticsilt-mehitamata-maismaasoidukid?id=91187393. Retrieved 29 September 2020.
- ↑ "Milrem Robotics delivers the TheMIS UGVs to Ukraine" (in English). 6 September 2022. https://milremrobotics.com/milrem-robotics-delivers-the-themis-ugv-to-ukraine/.
- ↑ "Milrem Robotics to deliver 14 TheMIS UGVs to Ukraine in cooperation with KMW" (in English). 29 November 2022. https://milremrobotics.com/milrem-robotics-to-deliver-14-themis-ugvs-to-ukraine-in-cooperation-with-kmw/.
- ↑ "Milrem Robotics delivers the first THeMIS to Australia". 22 April 2021. https://milremrobotics.com/milrem-robotics-delivered-the-first-themis-to-australia/.
- ↑ "Ei tarvitse kahvitaukoja – puolustusvoimat esitteli miehittämättömän maa-ajoneuvon ja dronen yhteistoimintaa tiedustelussa". 1 April 2022. https://yle.fi/uutiset/3-12382919.
- ↑ Saballa, Joe (2022-08-11). "Spain Receives First THeMIS Unmanned Ground Vehicle" (in en-US). https://www.thedefensepost.com/2022/08/11/spain-themis-unmanned-vehicle/.
- ↑ "UMEX 2020: Milrem showcases updated THeMIS UGV". Melanie Rovery. janes.com. 25 February 2020. https://www.janes.com/defence-news/news-detail/umex-2020-milrem-showcases-updated-themis-ugv.
 |