Engineering:BSV Luftikus
| Luftikus | |
|---|---|
| |
| Role | Single seat glider |
| National origin | Germany |
| Manufacturer | Berlin Segelflug-Verein (BSV) |
| Designer | Otto Hohmuth |
| First flight | May 1929 |
| Number built | 3 |
| Developed into | Windhund |
The BSV Luftikus was a German competition glider, designed for economy of construction and first flown in 1929. From 1929 to 1931 it took part in the annual national gliding contests held on the Wasserkuppe, often known as the Rhön contests.
Design and development
A relaxation in 1924 of the restrictions on aircraft building imposed on Germany after World War I allowed the development powered aircraft. Germany's relatively advanced glider constructors were concerned that this threatened to end their sport and some turned their attention to the possibilities of motor gliders. In about 1927 the Berlin Segelflug-Verein (BSV) began the design of such an aircraft with their new designer Otto Hohmuth. The target was a low cost machine for the 1928 Rhön contest, simple to build and without the long span wings of the highest performing gliders, but they underestimated the costs and construction time. An engine was never fitted and the final output, the Luftikus, first flew in May 1929.[1]
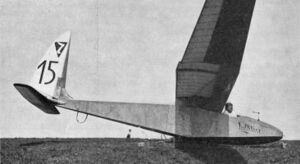
It was a parasol wing glider, though the three part wooden wing was a cantilever structure, held above the fuselage on two almost vertical streamlined steel struts from the fuselage, one on either side and by further central, vertical struts, faired in to form a slender ply skinned central pylon. The centre section was rectangular in plan, occupying about one third of the span; the outer sections were double tapered to semicircular tips. The wing was built around a single spar with plywood skin from it forward around the leading edge forming a torsion resistant box. On the centre section the ply skin extended rearwards to diagonal auxiliary spars and on the lower surface of the outer panels to the aileron hinge. The rest of the wing surface, including the long ailerons was fabric covered.[1]
The wood framed, unusually narrow fuselage was hexagonal in cross section forward of its deepest point under the wing but rectangular aft. The open cockpit positioned the pilot's headrest immediately under the wing leading edge. Aft, the fuselage tapered, more strongly in depth than height. The areas of the fin and tailplane were very small, but the rudder was broad and almost a quadrant, cut away below to allow operation of the long, narrow, balanced one piece elevator. The third example had some small rudder modifications, with a bigger hinge gap and a flatter top. Like the ailerons, the rear control surfaces were fabric covered. A 2 m (6 ft 7 in), rubber sprung landing skid reached back towards the wing trailing edge, assisted by a pair of looped tubes acting as a tail skid.[1]
Two other copies of the Luftikus were built. One was used by the Magdeburg police glider club and another, built by Hans Bohnert, was shot down during the German invasion of Norway .[1]
Operational history
At the 1929 Rhön the Luftikus was piloted by Otto Bedau who was only allowed to fly in the B category as he had not then achieved the five minutes of soaring flight required to compete in the highest class C.[1][2] He went on to win in the B class with flights of over six minutes and a maximum altitude of 610 m (2,000 ft). Bedau flew the Luftikus in the next two Rhöns, finishing runner-up in 1930. On the last day of that competition he was lifted by the updraught under a cumulus cloud to 1,640 m (5,380 ft) above ground, where the controls froze. Finally recovering control at 800 m (2,620 ft) he continued his flight, staying airborne for 7 hours and 34 minutes and landing after the end of the event. He also pioneered wire towed launches ("American wire cable flying") in Europe behind a car or powered aircraft and gave a demonstration of double aerotowing at the 1931 Rhön. Later, in Berlin, Bedau and the Luftikus were part of the first triple aerotow.[1]
Specifications
Data from Historische Deutsche Flugzeug bis 1945 [1]
General characteristics
- Crew: One
- Length: 6.40 m (21 ft 0 in)
- Wingspan: 15.00 m (49 ft 3 in)
- Height: 1.80 m (5 ft 11 in)
- Wing area: 15.40 m2 (165.8 sq ft)
- Aspect ratio: 14.6
- Airfoil: Göttingen 535
- Empty weight: 143 kg (315 lb)
- Gross weight: 214 kg (472 lb)
- wing loading: 13.9 kg/m2 (2.8 lb/sq ft)
Performance
- Rate of sink: 0.74 m/s (146 ft/min) minimum, at 50 km/h (31 mph)
See also
Related lists
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Kens, Karlheinz (2011) (in German). Historische Deutsche Flugzeug bis 1945 band 1. Baden-Baden: Modellsport Verlag GMBH. pp. 50–57. ISBN 978-3-923142-39-2. http://www.modellsport.de.
- ↑ Simons, Martin (2006). Sailplanes 1920-1945 (2nd revised ed.). Königswinter: EQIP Werbung & Verlag GmbH. pp. 47. ISBN 3 9806773 4 6.
External links
 |

