Engineering:Lioré et Olivier LeO H-180
From HandWiki
Short description: French flying-boat
| LeO H-180 | |
|---|---|

| |
| Role | Two-seat flying-boat |
| National origin | France |
| Manufacturer | Lioré et Olivier |
| First flight | 1928 |
| Number built | 6 |
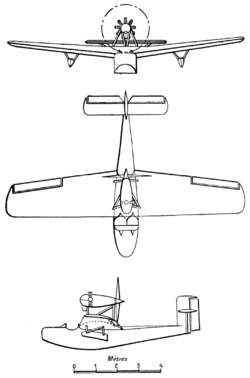
The Lioré et Olivier LeO H-180 was a 1920s France two-seat flying-boat built by Lioré et Olivier.[1]
Development
The H-180 first flew in 1928 and was a cantilever high-wing monoplane flying-boat.[1] Powered by a 120 hp (89 kW) Salmson 9Ac engine strut-mounted above the fuselage.[1] It had two side-by-side seats in an open cockpit but the following year it was fitted with an enclosed cockpit and re-designated the LeO H-181.[1] The company intended to build a production batch of ten aircraft but only five H-181s were built.[1] One aircraft was destroyed and the others finding no buyers were used as test aircraft by the company.[1]
Variants
- H-180
- Two-seat touring / training flying boat; 1 built.[2]
- H-181
- An enclosed cockpit version, with increased span and longer fuselage; 5 built.[3]
Specifications (H-180)
Data from Flight,[4] Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1928[5]
General characteristics
- Crew: 2, (1 pilot)
- Capacity: (1 pax)
- Length: 7.25 m (23 ft 9 in)
- Wingspan: 11.2 m (36 ft 9 in)
- Height: 2.2 m (7 ft 3 in)
- Wing area: 17.2 m2 (185 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 680 kg (1,499 lb)
- Gross weight: 960 kg (2,116 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Salmson 9Ac 9-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engine, 89 kW (120 hp)
- Propellers: 2-bladed fixed pitch pusher propeller
Performance
- Maximum speed: 165 km/h (103 mph, 89 kn)
- Cruise speed: 140 km/h (87 mph, 76 kn)
- Range: 520 km (320 mi, 280 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 3,500 m (11,500 ft)
- Time to altitude: 20 min to 2,000 m (6,600 ft)
- Wing loading: 55.8 kg/m2 (11.4 lb/sq ft)
- Power/mass: 0.09341 kW/kg (0.05682 hp/lb)
See also
Related lists
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft (Part Work 1982-1985). Orbis Publishing. p. 2334.
- ↑ Parmentier, Bruno (13 December 1998). "Lioré et Olivier LeO H-180, Hydravion d'entrainement par Aviafrance" (in fr). Pariz. https://www.aviafrance.com/aviafrance1.php?ID=615&ID_CONSTRUCTEUR=825&ANNEE=0&ID_MISSION=0&MOTCLEF=. Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- ↑ Parmentier, Bruno (13 December 1998). "Lioré et Olivier LeO H-181, Hydravion d'entrainement par Aviafrance" (in fr). Pariz. https://www.aviafrance.com/aviafrance1.php?ID=616&ID_CONSTRUCTEUR=825&ANNEE=0&ID_MISSION=0&MOTCLEF=. Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- ↑ "The Leo H.18". Flight XXI (29): 724–725. 18 July 1929. http://www.flightglobal.com/pdfarchive/view/1929/1929-1%20-%200417.html.
- ↑ Grey, C.G., ed (1928). Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1928. London: Sampson Low, Marston & company, ltd. p. 108c.
Bibliography
- Hartmann, Gérard. Les Avions Lioré Et Olivier. Boulogne-Billancourt, France: ETAI. 2002. ISBN:2-7268-8607-8 (in French)
 |