Engineering:Arrow Active
| Active | |
|---|---|

| |
| Arrow Active 2 | |
| Role | Aerobatic sports aircraft |
| Manufacturer | Arrow Aircraft Ltd. |
| Designer | A. C. Thornton |
| First flight | 1931 |
| Number built | 2 |
The Arrow Active is a British aerobatic aircraft built in the 1930s.
Design and development
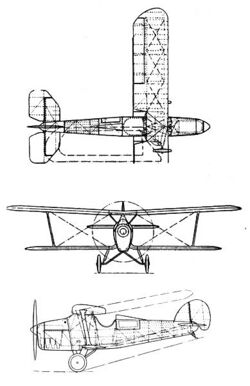
In 1930, Arthur Cecil Thornton, previously an aircraft designer with Blackburn Aircraft, set up his own company, Arrow Aircraft, at Leeds, Yorkshire, to develop his ideas for a single-seat aerobatic aircraft and advanced trainer.[1] The resulting design, the Arrow Active was a single-seat biplane of conventional configuration, with single-bay, staggered wings of unequal span and chord, bordering on being a sesquiplane. The upper and lower wings are joined by a single interplane strut. The undercarriage is fixed, with a pair of mainwheels and a tail-skid. It was originally powered by a 115 hp (86 kW) Cirrus-Hermes IIB engine.
The second aircraft built featured a more powerful 120 hp (90 kW) de Havilland Gipsy III and was designated Active 2. It also differed from the Active 1 in having a strutted, conventional centre section, a slightly different shaped fin and rudder, and smaller, wider wheels.
Operational history
Although it was originally hoped[2] that the military might show an interest in the aircraft, this did not transpire, and the Active was flown as a sports plane. The Active 1 G-ABIX received its Certificate of Airworthiness on 21 May 1931[3] and flew at 132.2 mph (212 km/h) in the 1932 King's Cup Race. It was Alex Henshaw's mount in the second half of 1935 until severely damaged in a crash following an in-flight fire that December.
The Active 2 G-ABVE was certified on 29 June 1932[4] and flew in the King's Cup in both 1932 and 1933. Slightly faster than the Arrow 1, it recorded a speed of 137 mph (220 km/h)
Variants
- Active 1
- One aircraft powered by a 115hp (86kW) Cirrus Hermes IIB engine.
- Active 2
- One aircraft powered by a 120hp (90kW) de Havilland Gipsy III engine, rebuilt in 1958 with a de Havilland Gipsy Major 1C.[5]
Surviving aircraft
Rebuilt in 1958, and again in 1989, the Active 2 is still on the British civil register and is based at Coventry, England.[6][citation needed]
Specifications (Active 2)
Data from [7]
General characteristics
- Crew: one pilot
- Length: 18 ft 10 in (5.74 m)
- Wingspan: 24 ft 0 in (7.32 m)
- Height: 7 ft 3 in (2.21 m) [8]
- Wing area: 120 sq ft (11.2 m2) [8]
- Empty weight: 925 lb (420 kg)
- Gross weight: 1,325 lb (600 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × de Havilland Gipsy III inverted inline engine , 120 hp (80 kW)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 144 mph (230 km/h, 125 kn)
- Cruise speed: 128 mph (206 km/h, 111 kn)
- Range: 420 mi (676 km, 360 nmi) [8]
References
Notes
- ↑ Ord-Hume 1977, p. 601
- ↑ Flight 24 July 1931, p. 727
- ↑ Jackson 1959, p. 407; Jackson 1973, p. 286
- ↑ Jackson 1959, p. 408; Jackson 1973, p. 287
- ↑ UK CAA/G-INFO
- ↑ "Register of Aircraft". https://www.caa.co.uk/register%20of%20aircraft/G-INFO.[|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
- ↑ Jackson 1959, pp. 407–408; Jackson 1973, pp. 206–207
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Ord-Hume 2000, pp. 234
Bibliography
- Ord-Hume, Arthur (November 1977). "British pre-war ultra-lights: No 20: Arrow Active". Aeroplane Monthly 5 (11): 600–604.
- Ord-Hume, Arthur W.J.G. (2000). British Light Aeroplanes. Peterborough: GMS Enterprises. ISBN 1-870384-76-8.
- Jackson, A.J. (1959). British Civil Aircraft 1919-59, volume 1. London: Putnam and Co. Ltd.
- Jackson, A.J. (1973). British Civil Aircraft since 1919 Volume 1. London: Putnam. ISBN 0-370-10006-9.
- "The Arrow "Active"". Flight XXIII (1178): 727–730. 24 July 1931. https://archive.org/details/Flight_International_Magazine_1931-07-24-pdf/page/n25/mode/2up. Retrieved 8 January 2024.
- Taylor, Michael J. H. (1989). Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation. London: Studio Editions.
- World Aircraft Information Files. London: Bright Star Publishing.
 |