Engineering:Kampfpistole
| Kampfpistole | |
|---|---|
 This photo is of a Leuchtpistole 34. The Kampfpistole was nearly identical except it had a rifled barrel. | |
| Type | Flare gun |
| Place of origin | |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1939-1945 |
| Used by | Germany |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Walther |
| Manufacturer | Walther Erma |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 1.4 kg (3 lb 1 oz) |
| Length | 155 mm (6.1 in)[1] |
| Cartridge | Fallschirm Leuchtpatrone Nebelpatrone Sprengpatrone |
| Calibre | 23 mm (0.91 in) |
| Action | Break action |
| Feed system | Single shot[1] |
The Kampfpistole or "combat pistol" in English was a flare gun introduced into German service during 1939 and served throughout World War II.
Design
The Kampfpistole was a single shot, break action, flare gun designed and produced by Walther that was a variant of the earlier Leuchtpistole 34. Externally both the Kampfpistole and the Leuchtpistole 34 were nearly identical. The difference between the two models was the Kampfpistole had a rifled barrel while the Leuchtpistole 34 was a smoothbore gun. The Kampfpistole could be identified by a Z engraved on the barrel of the gun. The Kampfpistole's frame was machined from duralumin, the barrel was machined from steel, was blued to stop corrosion, and had bakelite pistol grips.[1]
Ammunition
The primary roles for the Kampfpistole were signaling, illumination, target marking, or concealment with a smoke grenade. Later during World War II, explosive rounds were developed to give German troops a small and lightweight grenade launcher for engaging targets from close range which could not be engaged satisfactorily by infantry weapons or artillery without endangering friendly troops.[2]
Available projectiles included:
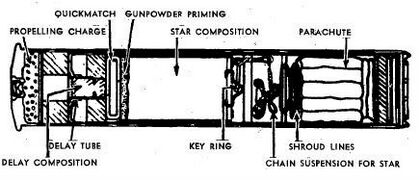
- Fallschirm Leuchtpatrone - This was a non-lethal parachute retarded flare that could be used for battlefield illumination or as a signal flare. The projectile can be identified by its "F. Leucht. Z." marking on the base of the projectile.[3]
- Nebelpatrone - This was a non-lethal smoke grenade with a nose fuze that could be used for target marking or concealment. It was similar in appearance to explosive grenades and could be identified by its "NEBEL. Z" marking on the base of the projectile.[3]
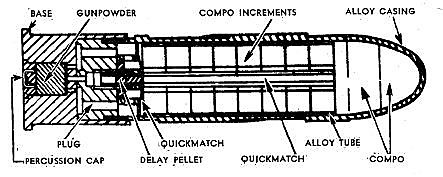
- Sprengpatrone - A nose fuzed high explosive grenade that was used for low angle direct fire where range and accuracy were needed. It was not recommended for use beyond 180 m (200 yd) due to inaccuracy or less than 46 m (50 yd) due to the risk from shell fragments.[2]
Gallery
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Mod. Kampfpistole". http://leuchtpistole.free.fr/Sommaire/En_ModeleKampfpistole.html.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 United States. War Department. Military Intelligence Division (1943-01-01). Tactical And Technical Trends, Nos. 21-30. https://archive.org/details/TacticalAndTechnicalTrendsNos21-30-nsia.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 unknown (1 August 1945). Catalog Of Enemy Ordnance Material. www.paperlessarchives.com/FreeTitles/CatalogOfEnemyOrdnanceMateriel.pdf: Office of the chief of ordnance. pp. 326.
 |