Engineering:Satellite bus
A satellite bus (or spacecraft bus) is the main body and structural component of a satellite or spacecraft, in which the payload and all scientific instruments are held.
Bus-derived satellites are different to specially produced satellites. Bus-derived satellites are usually customized to customer requirements, for example with specialized sensors or transponders, in order to achieve a specific mission.[1][2][3][4]
They are commonly used for geosynchronous satellites, particularly communications satellites, but are also used in spacecraft which occupy lower orbits, occasionally including low Earth orbit missions.
Examples
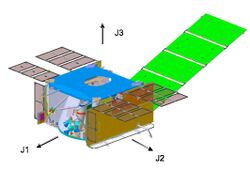
Some satellite bus examples include:
- Boeing DS&S 702
- Lockheed Martin Space Systems A2100
- Alphabus
- INVAP ARSAT-3K
- Airbus D&S Eurostar
- ISRO's I-1K, I-2K, I-3K, I-4K, I-6K, and Indian Mini Satellite bus
- NASA Ames MCSB
- SSL 1300
- Orbital ATK GEOStar
- Mitsubishi Electric DS2000
- Spacecraft bus of the James Webb Space Telescope
- SPUTNIX TabletSat
- SPUTNIX OrbiCraft-Pro
Components
A bus typically consists of the following subsystems:[6]
- Command and data handling (C&DH) system
- Communications system and antennas
- Electrical power system (EPS)
- Propulsion
- Thermal control
- Attitude control system (ACS)
- Guidance, navigation, and control (GNC) system
- Structures and trusses
- Life support (for crewed missions).
See also
References
- ↑ "TU Delft: Spacecraft bus subsystems". Lr.tudelft.nl. http://www.lr.tudelft.nl/en/organisation/departments/space-engineering/space-systems-engineering/expertise-areas/spacecraft-engineering/design-and-analysis/configuration-design/subsystems/subsystems/.
- ↑ "Spacecraft Systems". Braeunig.us. http://www.braeunig.us/space/systems.htm.
- ↑ "The James Webb Space Telescope". Jwst.nasa.gov. http://jwst.nasa.gov/bus.html.
- ↑ "Antrix Corporation Ltd - Satellites > Spacecraft Systems & Sub Systems". Antrix.gov.in. 2009-09-24. http://www.antrix.gov.in/sss_systems.html.
- ↑ "Status of the JWST Sunshield and Spacecraft". https://static1.squarespace.com/static/54b171c5e4b047061239404b/t/57b30618b8a79bb69fff7b4c/1471350297818/SPIE990405_Status+of+the+JWST+Sunshield+and+Spacecraft.pdf.
- ↑ Satellite Bus Subsystems , NEC, accessed 25 August 2012.
External links
- Satellite Glossary
- JWST Observatory: The Spacecraft Bus
- Spitzer's Spacecraft Bus
- Gunter's Space Page: Spacecraft buses
es:Satélite artificial#Modelo de satélite
 |