Medicine:ISET Test
| ISET Test | |
|---|---|
| Medical diagnostics | |
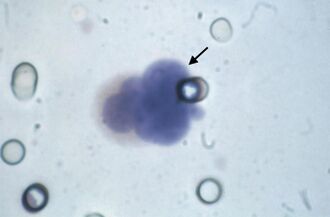 A circulating tumor cell (arrow) diagnosed by the ISET test. (The pores of the filter are also visible.) | |
| Purpose | Detect tumor cells |
| Test of | Blood |
The ISET Test (Isolation by SizE of Tumor cells / Trophoblastic cells) is a diagnostic blood test that detects circulating tumor cells in a blood sample.[1][2][3][4] The test uses an in-vitro diagnostic system developed at INSERM, the Université Paris Descartes and Assistance Publique Hôpitaux de Paris (AP-HP) in order to isolate cancer cells from blood without loss and identify them through a diagnostic cytopathology-based approach.
Operation
A 1-ml sample of blood will typically contain 5 to 10 million leukocytes, 5 billion erythrocytes, and a small number of circulating rare cells, including:
- non-tumor cells such as epithelial-normal cells, epithelial-atypical cells, endothelial vells and stem cells;
- physiological state-dependent cells such as fetal cells in pregnant and ex-pregnant women;
- circulating tumor cells (CTCs) which are of diagnostic value in diagnosing various cancers.
The diagnostic problem is to find and identify the rare CTCs among the abundant other cells in a given blood sample.
The ISET technology is based on the observation that tumor cells of all types of solid cancers are larger than blood cells (leukocytes and erythrocytes). However, blood filtration to recover rare circulating tumor cells without loss and without cell damage is a challenge. The ISET test uses a specially designed device and specially designed filters to allow the elimination of all erythrocytes and most leukocytes from the sample, making the subsequent cytopathology process significantly easier and more accurate.
History
The ISET technology was first reported in 2000 in the American Journal of Pathology by the team of Professor Patrizia Paterlini-Bréchot.
Since the first report in 2000, over 80 scientific articles have been published using the Rarecells System verifying the findings of the initial developers.
From 2005 to 2008, the device operating the ISET process was distributed by Metagenex. In 2009 Metagenex gave back the licences of the ISET patents to its developers: INSERM, University Paris Descartes and AP-HP. Paterlini-Bréchot then founded the company Rarecells[5] which, since 2010, has the exclusive licence of the ISET patents, distributes the ISET products and develops the ISET tests.
Sources
- ↑ "IsetbyRarecells". http://www.isetbyrarecells.com.
- ↑ "ISET : une prise de sang précoce pour dépister des maladies génétiques" par Inserm dans Futura Santé du 13 décembre 2012.
- ↑ "ISET : un test génétique prénatal à encadrer par Floriane Blanc dans Pour la science de novembre 2013.
- ↑ "Cancer : une nouvelle méthode pronostique non invasive testée sur le cancer du foie" par INSERM dans Caducee.net du12 mai 2004.
- ↑ "ISET Publications" by Rarecells in Rarecells Diagnostics.


