Medicine:Uremic frost
From HandWiki
Short description: Crystallized urea deposits on skin
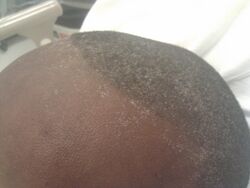
Uremic frost is a colloquial description for crystallized urea deposits that can be found on the skin of those affected by chronic kidney disease (CKD).[1] In states of prolonged kidney failure and subsequent uremia, the high level of urea in the bloodstream leads to high levels of urea secreted by eccrine sweat glands as a component of sweat. As water evaporates off the skin, it results in crystallization of the remaining urea.[citation needed]
This condition is more common in severe, untreated uremia and is associated with serum BUN levels >200. It is becoming rare in people with chronic kidney disease managed on long-term hemodialysis, with estimated prevalence between 0.8 and 3%.[2][3][4]
References
- ↑ Dennis, Mark; Bowen, William Talbot; Cho, Lucy (2012). "Uraemic frost". Mechanisms of Clinical Signs. Elsevier. p. 556. ISBN 978-0729540759. https://books.google.com/books?id=FIV-NYPRCzEC&pg=PA556; pbk
- ↑ Lynde, Carrie; Kraft, John. "Skin manifestations of kidney disease". http://www.parkhurstexchange.com/clinical-reviews/ct_02_vol15.
- ↑ "Skin changes in patients with chronic renal failure". Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 22 (2): 268–72. March 2011. PMID 21422624.
- ↑ "Cutaneous manifestations in patients with chronic renal failure on hemodialysis". Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 72 (2): 119–25. 2006. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.25636. PMID 16707817.
 |