Medicine:Craniometaphyseal dysplasia
| Craniometaphyseal dysplasia | |
|---|---|
 | |
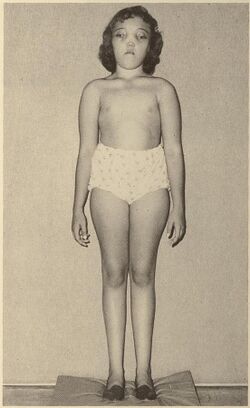
| Girl with craniometaphyseal dysplasia | |
| Specialty | Orthopedic |
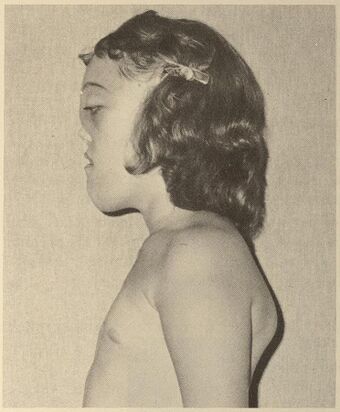
Craniometaphyseal dysplasia is a rare skeletal disorder that results from a mutation in the ANKH or GJA1 genes. The condition is characterized abnormal facial features, impairment of cranial nerves, and malformation of the long bones in the limbs.[1]
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms include:[1]
- Eating and breathing difficulties
- Hypertelorism
- Wide nasal bridge
- Large lower jaw
- Proptosis
- Dolichocephaly
- Delayed or absent teeth
- Small nasal passage
Long-term severe effects from untreated head and face pressure include cranial nerve paralysis, hearing loss/deafness, and blindness.
Genetics
The autosomal dominant form is caused by a mutation in ANKH on chromosome 5 (5p15.2-p14.1). The autosomal recessive form is caused by a mutation in a mutation in GJA1 on chromosome 6 (6q21-q22).[1] The recessive form tends to be more severe than the dominant form.[2]
Diagnosis
Craniometaphyseal dysplasia is diagnosed based on clinical and radiographic findings that include hyperostosis. Some things such as cranial base sclerosis and nasal sinuses obstruction can be seen during the beginning of the child's life. In radiographic findings the most common thing that will be found is the narrowing of foramen magnum and the widening of long bones. Once spotted treatment is soon suggested to prevent further compression of the foramen magnum and disabling conditions.[citation needed]
Treatment
The only treatment for this disorder is surgery to reduce the compression of cranial nerves and spinal cord. However, bone regrowth is common since the surgical procedure can be technically difficult. Genetic counseling is offered to the families of the people with this disorder.[3][4]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Craniometaphyseal Dysplasia". https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/craniometaphyseal-dysplasia/.
- ↑ "Craniometaphyseal dysplasia, autosomal dominant | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program". https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/1581/craniometaphyseal-dysplasia-autosomal-dominant.
- ↑ "Craniometaphyseal Dysplasia". http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/craniometaphyseal-dysplasia. Retrieved 16 April 2015.
- ↑ Reichenberger E (1993). Craniometaphyseal Dysplasia, Autosomal Dominant. University of Washington, Seattle. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1461/. Retrieved 16 April 2015.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
 |