Medicine:Ganglion cell layer
From HandWiki
Short description: Part of the retina of the eye
| Ganglion cell layer | |
|---|---|
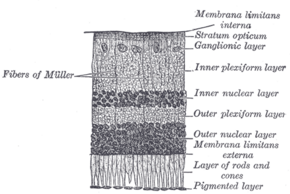 Section of retina. (Ganglionic layer labeled at right, third from the top.) | |
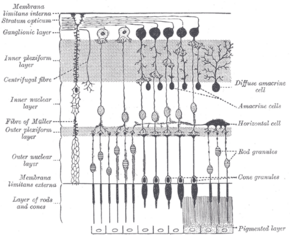 Plan of retinal neurons. (Ganglionic layer labeled at left, third from the top.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | stratum ganglionicum retinae |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In the anatomy of the eye, the ganglion cell layer (ganglionic layer) is a layer of the retina that consists of retinal ganglion cells and displaced amacrine cells.
The cells are somewhat flask-shaped; the rounded internal surface of each resting on the stratum opticum, and sending off an axon which is prolonged into it.
From the opposite end numerous dendrites extend into the inner plexiform layer, where they branch and form flattened arborizations at different levels.
The ganglion cells vary much in size, and the dendrites of the smaller ones as a rule arborize in the inner plexiform layer as soon as they enter it; while those of the larger cells ramify close to the inner nuclear layer.
References
External links
- Histology image: 07902loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
 |

