Medicine:Steroid-induced skin atrophy
| Steroid-induced skin atrophy | |
|---|---|
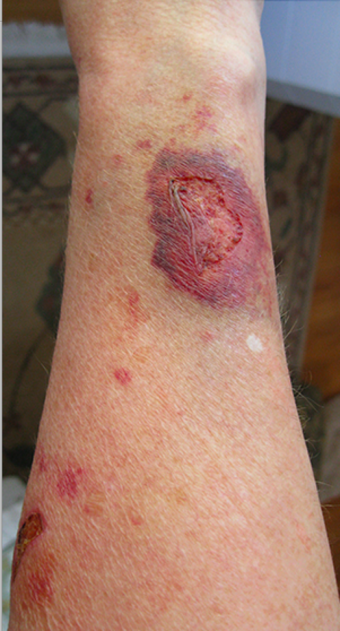 | |
| Skin atrophy | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | telangiectasias,[1] purpura, striae, hypopigmentation[2] |
| Complications | Possible HPA axis involvement[2] |
| Usual onset | within the first 7 days of daily superpotent TCS application under occlusion, within 2 weeks of daily use of less potent TCS or superpotent TCS without occlusion.[2] |
| Causes | Changes in gene regulation and transcription of various mRNA[2] |
| Risk factors | higher potency corticosteroids, more frequent application, extended duration of treatment,[3] use of occlusion, infancy/childhood, location[2] |
| Diagnostic method | Visual inspection of skin for visible signs of skin atrophy[1] |
| Prevention | Intermittent maintenance therapy; increasing duration of interval between applications[4] |
| Management | Discontinuation of treatment |
| Prognosis | Most signs of atrophy resolve by 1 to 4 weeks after discontinuation of the TCS; striae are permanent[2] |
| Frequency | up to 5% after a year of use (in psoriasis)[5] |
Steroid-induced skin atrophy is thinning of the skin as a result of prolonged exposure to topical steroids. In people with psoriasis using topical steroids it occurs in up to 5% of people after a year of use.[5]
Skin atrophy can occur with both prescription and over the counter steroids creams.[6] Low doses of prednisone by mouth can also result in skin atrophy.
Signs and symptoms
It can also present with telangiectasia, easy bruising, purpura, and striae. Occlusive dressings and fluorinated steroids both increase the likelihood of developing atrophy.[7]
Prevention
In general, use a potent preparation short term and weaker preparation for maintenance between flare-ups. While there is no proven best benefit-to-risk ratio,[8] if prolonged use of a topical steroid on a skin surface is required, a pulse therapy should be undertaken.
Pulse therapy refers to the application of a corticosteroid for 2 or 3 consecutive days each week or two. This is useful for maintaining control of chronic diseases. Generally a milder topical steroid or non-steroid treatment is used on the in-between days.[9]
Strong steroids should be avoided on sensitive sites such as the face, groin and armpits. Even the application of weaker or safer steroids should be limited to less than two weeks on those sites.
Treatment
The obvious priority is immediate discontinuation of any further topical corticosteroid use. Protection and support of the impaired skin barrier is another priority. Eliminating harsh skin regimens or products will be necessary to minimize potential for further purpura or trauma, skin sensitivity, and potential infection. Steroid-induced skin atrophy[10][11] is often permanent, though if caught soon enough and the topical corticosteroid discontinued in time, the degree of damage may be arrested or slightly improve. However, while the accompanying telangiectasias may improve marginally, the stretch marks are permanent and irreversible.[12]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Vázquez-López, F; Marghoob, AA (November 2004). "Dermoscopic assessment of long-term topical therapies with potent steroids in chronic psoriasis.". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 51 (5): 811–3. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.05.020. PMID 15523365.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Camisa, Charles; Garofola, Craig (2021). "Topical Corticosteroids". Comprehensive Dermatologic Drug Therapy: 511–527.e6. doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-61211-1.00045-0. ISBN 9780323612111.
- ↑ Takeda, K; Arase, S; Takahashi, S (1988). "Side effects of topical corticosteroids and their prevention.". Drugs 36 (Suppl 5): 15–23. doi:10.2165/00003495-198800365-00005. PMID 3076129.
- ↑ Lubach, D; Rath, J; Kietzmann, M (1995). "Skin atrophy induced by initial continuous topical application of clobetasol followed by intermittent application.". Dermatology 190 (1): 51–5. doi:10.1159/000246635. PMID 7894098.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Castela, E; Archier, E; Devaux, S; Gallini, A; Aractingi, S; Cribier, B; Jullien, D; Aubin, F et al. (May 2012). "Topical corticosteroids in plaque psoriasis: a systematic review of risk of adrenal axis suppression and skin atrophy.". Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 26 (Suppl 3): 47–51. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2012.04523.x. PMID 22512680.
- ↑ Abraham, A; Roga, G (September 2014). "Topical steroid-damaged skin.". Indian Journal of Dermatology 59 (5): 456–9. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.139872. PMID 25284849.
- ↑ "Disorders of collagen, Weedon's Skin Pathology (Third Edition), 2010: CORTICOSTEROID ATROPHY".
- ↑ Last, Allen R.; Ference, Jonathan D. (2009-01-15). "Choosing Topical Corticosteroids". American Family Physician 79 (2): 135–140. PMID 19178066. http://www.aafp.org/afp/2009/0115/p135.html.
- ↑ "Course on topical steroids". http://dermnetnz.org/doctors/dermatitis/corticosteroids.html.
- ↑ Fukaya, Mototsugu (2000). Color Atlas of Steroid Withdrawal from Corticosteroids in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. Tokyo, Japan: Ishiyaku Publishers, Inc.. http://www.tclinic.jp/atopy/eng/eng.html. Retrieved 2014-12-23.
- ↑ Fukaya, Mototsugu (June 2000). Atopic Dermatitis and Steroid Withdrawal (1st ed.). Japan: Ishiyaku Pub, Inc.. p. 107. (skin atrophy caused during application of the steroid ointment). ISBN 978-4-263-20140-4. http://www.ishiyaku.co.jp/search/details.aspx?bookcode=201400.
- ↑ "Steroid Atrophy". http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/470168.
 |


