Earth:Foredune
A foredune is a dune ridge that runs parallel to the shore of an ocean, lake, bay, or estuary. Foredunes consist of sand deposited by wind on a vegetated part of the shore. Foredunes can be classified generally as incipient or established.[1]
Formation
Foredunes may begin as shadow dunes that form in the wind shadows of clumps of vegetation.[2] Several shadow dunes may eventually join to form an incipient foredune.[3] When an incipient foredune reaches a height of about 1.5 feet (0.5 m), it has a significant wind shadow of its own. Wind-blown sand will tend to fall on this incipient dune rather than traveling further inland. When a foredune becomes 3 to 5 feet (0.9 to 1.5 m) high, it may trap all of the wind-blown sand from the beach.[4]
In active dune systems, the foredunes appear closest to the sea or other body of water. However, some dune systems, such as those on eroding coasts, do not have foredunes. In those systems, other kinds of dunes may be closest to the water.[1]
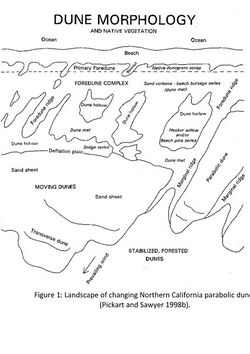
A foredune ecosystem begins with the first dune ridge directly behind an active beach. The ridge of a foredune can range in height from a few meters to tens of meters tall. Foredunes are formed when sand accumulates and wind actively transforms the landscape. This results in sand sheets can consuming in-land ecosystems. United States Fish and Wildlife Service actively manages Humboldt Bay's Lanphere Dunes. Active sand sheets at Lanphere Dunes have been measured to be in excess of six hundred meters.
Parabolic dunes in Northern California
Parabolic dunes are identified by vegetated dune ridges and vegetated deflated plains. Due to variable wind gusts, parabolic dunes are commonly unvegetated in troughs or dune swells where wind tunnels transport currents. Ripple alignment in association with the main dunes can also identify parabolic dunes. Ripples minuet accumulations of sand against the main dune swale. The heights of ripples are normally measured on a millimeter to centimeter scale. In Humboldt Bay, the wind is predominately blowing in from the northwest. As a result, the dune ridges are formed parallel to the wind currents while ripples are formed perpendicular to the wind.
Wind
Northern California coastal dune environments are subject to high velocity winds at all times throughout the year. This strong variable causes the morphology of the dune ecosystem to constantly change. Dunes can range in height from a meter to tens of meters tall creating elevation changes and habitat complexities. Invasive species can further armor dune ridges, creating linear dunes, and preventing naturalistic parabolic dunes from being created.
Sediment transport
Sand granules are transported in three ways: suspension, saltation, and creep. Suspended grains are fine granules that can easily be picked up by wind and carried for variable distances. Most visitors to coastal beach environments can attest to having sand blown in their face or leaving with a gritty feeling on their skin. This is due to fine sediment suspended in the moisture rich air. When suspended sediment is returned to the ground, granules physically impact the grounded grains. Due to physics principles, the grounded grains are receiving energy from the once suspended sediment. This impact leads to the dislodgement of grounded grains or creep of coarser grains.[6] Saltation is the movement of grains being picked up by the wind and dropped in a cycling repetitive motion.
Sources of sediment
Coastal environments act as drainage outlets for freshwater river systems. As a result, sediment from tributaries and headwaters are deposited at the mouth of the river. Long shore transport is a linear current off the coastline that moves sediment. For Northern California, this current moves sediment in a northern direction. Therefore, sand and sediment constructing Humboldt Bay's thirty-four mile dune ecosystem, is a result of sediment deposition at a southern location.[7]
Sediment accumulation can also be a result of wave action. Wave currents occur in a swash and backwash motion. This continual wave action allows for the movement of sediment. The angles at which the swash and backwash occur, are associated with the off shore transport current as well as the change in winter and summer ocean currents.
Foredune ecology
The vegetation analyzed at the Mad River County Beach showed an evolutionary change in the ecosystem as a result of several thriving invasive species. Upon arrival to the beach, it became visually apparent just how abundant the Ammophila arenaria (European beach grass) species is. According to Pickart and Sawyer (1998), Ammophila arenaria is described as being foredune engineers. As Ammophila arenaria attaches and begins to grow on a relatively flat dune system, wind currents that push sand inland it allows the plant to accumulate and mound massive amounts of sand creating large foredune ridges.[8]
This shift is supporting the invasion of but not limited to, Ammophila arenaria, Tanacetum vulgare (tansy) and Bromus diandrus (ripgut brome). Since introduction of these invasive plants, scientists have recorded a severe displacement in native grasses and dune mat vegetation throughout California. A characteristic of Ammophila arenaria and Bromus diandrus entering an ecosystem, are elevated levels of nitrogen within the soil [8] . Unfortunately, the implementation of nitrogen into the soil, limits the growth and livelihood of other species such as Layia carnosa and Erysimum menziesii.
Since the early 1900s, Ammophila arenaria has been introduced into the California landscape to perform as a natural re-engineering feature to transform the beach landscape.[8] In areas without Ammophila arenaria, dune mat vegetation was relatively abundant and thriving. This data shows that with active restoration efforts to combat invasive species, land managers could sustain a healthy native vegetation population and thus transform the landscape back to its native habitat. Understanding how invasive species change and manipulate landscapes and the characteristics of specific invasive species, is the best way to reduce impacts and restore ecosystems for native species.
Ammophila arenaria is an ecosystem engineer that has the ability to displace native dune mat vegetation by transforming historical dune ecology.[5] Removal of Ammophila arenaria presents a daunting task for land managers and restoration teams. Ammophila arenaria has evolved to grow in“vigorous root and rhizome systems”.[8] Research shows that these root systems can be in excess of ten feet.[9]
Characteristically, Ammophila arenaria invades the historically flat Californian foredunes transforming the ecology of the dune system. As wind currents push sand inland, the Ammophila arenaria begins to accumulate massive amounts of sand creating large foredune ridges.[5] The alteration of dune morphology affects native plants and animal species that rely heavily on the dunes for nourishment and habitat.[8]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Hesp, Patrick (2002). "Foredunes and blowouts: initiation, geomorphology and dynamics". Geomorphology 48 (1–3): 245–268. doi:10.1016/S0169-555X(02)00184-8. Bibcode: 2002Geomo..48..245H. http://www.ga.lsu.edu/hesp/PDFs/Geomo02.pdf. Retrieved 2012-12-11.
- ↑ "Lake Michigan Coastal Dunes: Shadow Dunes". Calvin College. http://www.calvin.edu/academic/geology/coastaldunes/dunes/foredunes2.htm.
- ↑ "Lake Michigan Coastal Dunes: Foredunes". Calvin College. http://www.calvin.edu/academic/geology/coastaldunes/dunes/foredunes1.htm.
- ↑ "Lake Michigan Coastal Dunes: Active Foredunes". Calvin College. http://www.calvin.edu/academic/geology/coastaldunes/dunes/foredunes4.htm.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Pickart, A.; Sawyer, J. (1998). Invasive Plant Species. California Native Plant Society. pp. 41–55.
- ↑ Bierman, P.; Montgomery, D. R. (2014). Chapter 10: Wind as a Geomorphic Agent: Key Concepts in Geomorphology. W. H. Freeman and Company Publishers. pp. 329–354.
- ↑ Friends of the Dunes (n.d.). Coastal Naturalist Manual. Friends of the Dunes.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 Pickart, A.; Sawyer, J. (1998). Ecology and Restoration of Northern California Coastal Dunes. California Native Plant Society. pp. 1–36.
- ↑ Humboldt County Weed Management Area (2010). Invasive Weeds of Humboldt County: A Guide for Concerned Citizens. Arcata, California.
 |

