Earth:Jut (topography)
In topography, jut is a measure of the base-to-peak rise and visual impressiveness of a mountain summit or other landform. It describes how sharply or impressively a location rises above surrounding terrain by factoring both height above surroundings and steepness of ascent.[1]
Description
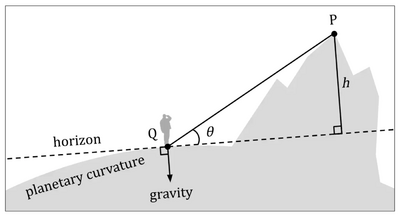
A mountain with a jut of X can be interpreted to rise as sharply or impressively as a vertical cliff of X. For example, a vertical cliff of height 100 meters, a 45° slope of height 141 meters, and a 30° slope of height 200 meters all measure a jut of 100 meters and can be interpreted to rise equally sharply. Jut can be further decomposed into base-to-peak height and base-to-peak steepness, where jut equals base-to-peak height multiplied by the sine of base-to-peak steepness.
Definition
Jut [math]\displaystyle{ J=\max{H'} }[/math] is the maximum angle-reduced height (symbol H'), which can be defined as the vector projection, in the line of sight, of the peak's height (or vertical separation), H:[2][3]
- [math]\displaystyle{ H'=H|\sin{e}| }[/math]
where e is the summit's elevation angle. Height, angle-reduced height, and jut have unit of length (meter or feet). While height and angle-reduced height depend on the viewing location around the peak, jut is a constant value for a given peak.[1] Base is the location where angle-reduced height is maximized.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Glossary of Terms - Peakbagger.com". https://www.peakbagger.com/help/glossary.aspx.
- ↑ Xu, Kai (2022-08-02). "Beyond Elevation: New Metrics to Quantify the Relief of Mountains and Surfaces of Any Terrestrial Body". Cornell ArXiv. https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.01600.
- ↑ "About | PeakJut". https://peakjut.com/about.
 |